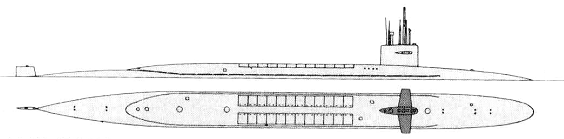

Henry M. Jackson 2000
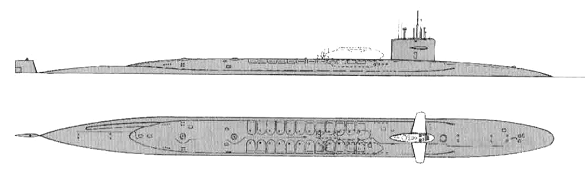
Ohio 2010
| No | Name | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comm | Fate |
| SSBN726, 10.2002- SSGN726 | Ohio | 216 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 10.4.1976 | 7.4.1979 | 11.11.1981 | guided-missile nuclear-powered submarine 12.2005, in service (2020) |
| SSBN727, 1.2004- SSGN727 | Michigan | 222 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 4.4.1977 | 26.4.1980 | 11.9.1982 | guided-missile nuclear-powered submarine 6.2009, in service (2020) |
| SSBN728, 10.2002- SSGN728 | Florida | 223 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 19.1.1981 | 14.11.1981 | 18.6.1983 | guided-missile nuclear-powered submarine 3.2006, in service (2020) |
| SSBN729, 3.2004- SSGN729 | Georgia | 224 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 7.4.1979 | 6.11.1982 | 11.2.1984 | guided-missile nuclear-powered submarine 2008, in service (2020) |
| SSBN730 | Henry M. Jackson (ex-Rhode Island) | 225 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 19.11.1981 | 15.10.1983 | 6.10.1984 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN731 | Alabama | 226 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 27.8.1981 | 19.5.1984 | 25.5.1985 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN732 | Alaska | 227 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 9.3.1983 | 12.1.1985 | 25.1.1986 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN733 | Nevada | 230 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 8.8.1983 | 14.9.1985 | 16.8.1986 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN734 | Tennessee | 231 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 9.6.1986 | 13.12.1986 | 17.12.1988 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN735 | Pennsylvania | 234 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 2.3.1987 | 23.4.1988 | 9.9.1989 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN736 | West Virginia | 235 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 14.10.1989 | 18.12.1987 | 20.10.1990 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN737 | Kentucky | 238 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 18.12.1987 | 11.8.1990 | 13.7.1991 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN738 | Maryland | 242 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 22.4.1986 | 10.8.1991 | 13.6.1992 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN739 | Nebraska | 243 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 6.7.1987 | 15.8.1992 | 10.7.1993 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN740 | Rhode Island | 248 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 15.9.1988 | 17.7.1993 | 9.7.1994 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN741 | Maine | 249 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 3.7.1990 | 16.7.1994 | 29.7.1995 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN742 | Wyoming | 251 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 8.8.1991 | 15.7.1995 | 13.7.1996 | in service (2020) |
| SSBN743 | Louisiana | 254 | General Dynamics, Electric Boat Div., Groton | 23.10.1992 | 27.7.1996 | 6.9.1997 | in service (2020) |
| Data variant | as commissioned |
|
Displacement standard, t |
12500 (light) |
|
Displacement normal, t |
16764 / 18750 |
|
Length, m |
170.7 |
|
Breadth, m |
12.8 |
|
Draught, m |
11.1 |
|
No of shafts |
1 |
|
Machinery |
2 sets geared steam turbines, 1 General Electric S8G nuclear reactor |
|
Power, h. p. |
35000 |
|
Max speed, kts |
/ 25 |
|
Fuel, t |
nuclear |
|
Endurance, nm(kts) |
practically unlimited |
|
Armament |
SSBN726-733: 24 Trident C-4 SLBM (UGM-96A), 4 - 533 Mk 68 TT (bow) SSBN734-743: 24 Trident D-5 SLBM (UGM-133A), 4 - 533 Mk 68 TT (bow) |
|
Electronic equipment |
SSBN726-737: BPS-15H radar, BQQ-5E(v)4 or BQQ-6 passive sonar suite, BQS-13, BQS-15 sonars, BQR-15 sonar with TB-23 towed array, BQR-19 sonar, BQQ-9 TASPE sonar, WLR-8(V)5 ECM suite, WLR-10 radar interceptor, 8 CSA Mk 1 decoy launchers, CCS Mk 2 CCS SSBN738-740: BPS-15H radar, BQQ-5E(v)4 or BQQ-6 passive sonar suite, BQS-13, BQS-15 sonars, BQR-15 sonar with TB-23 towed array, BQR-19 sonar, BQQ-9 TASPE sonar, WLR-8(V)5 ECM suite, WLR-10 radar interceptor, 14 CSA Mk 2 decoy launchers, CCS Mk 2 CCS SSBN741-743: BPS-16(V) radar, BQQ-5E(v)4 or BQQ-6 passive sonar suite, BQS-13, BQS-15 sonars, BQR-15 sonar with TB-23 towed array, BQR-19 sonar, BQQ-9 TASPE sonar, WLR-8(V)5 ECM suite, WLR-10 radar interceptor, 14 CSA Mk 2 decoy launchers, CCS Mk 2 CCS |
|
Complement |
163 |
|
Diving depth operational, m |
300 |
Project history: These are by far the largest US submarines, although they are overshadowed by the Soviet Akulas. They differ from earlier US strategic submarines in having twenty-four rather than sixteen missiles, and incorporate a bow sonar (BQQ-6, similar to BQQ-5 but without active elements) and torpedo tubes set back from the bow, as in the newer attack submarines. The S8G reactor is a natural circulation type, related to the S5G in the Narwhal. Ohio class submarines were planned to operate 70-day patrols, with 25-day refit periods between patrols (shortened by the provision of special access trunks into the hull), with a 20-monih refit every nine years, for an overall force availability of 66%, compared to 55% of Poseidon submarines. Really deployment average is 77 days with 35 days in the homeport. Each submarine has two equal crews for year-round operations. The entire programme has suffered from severe delays. Ohio did not run trials until June 1981, although delivery was originally scheduled for December 1977.
Modernizations: 2002, Alaska; 2003, Nevada; 2005, Henry M. Jackson; 2008, Alabama: - 24 Trident C-4 SLBM (UGM-96A); + 24 Trident D-5 SLBM (UGM-133A)
12/2005, Ohio; 4.2006, Florida; 11.2006, Michigan; 11.2007, Georgia: were converted to cruise-missile submarines with data as given in the table.
| Data variant | SSGN conversion |
|
Displacement standard, t |
|
|
Displacement normal, t |
16764 / 18750 |
|
Length, m |
170.7 |
|
Breadth, m |
12.8 |
|
Draught, m |
11.1 |
|
No of shafts |
1 |
|
Machinery |
2 geared steam turbines, 1 General Electric S8G nuclear reactor |
|
Power, h. p. |
35000 |
|
Max speed, kts |
/ 25 |
|
Fuel, t |
nuclear |
|
Endurance, nm(kts) |
practically unlimited |
|
Armament |
22 Tomahawk CruM VLS (154 Tomahawk Block III or Tactical Tomahawk UGM-109 CruM), 4 - 533 Mk 68 TT (bow, Mk 48 torpedoes, UUVs) |
| Military load | 2 midget submarines or 2 DDS (Dry Deck Shelters, carrying LSDV swimmer delivery vehicle), 66-man SEAL force (102 max) |
|
Electronic equipment |
BPS-16(v)4 radar, BQQ-5E(v)4 passive sonar suite, BQS-13, BQS-15 sonars, BQR-15 sonar with TB-23 towed array, BQR-19 sonar, BQQ-9 TASPE sonar, BLQ-10(v) ECM suite, 4 CSA Mk 1 decoy launchers, CCS Mk 2 Mod. 3 CCS |
|
Complement |
140 + 66-102 SEALs |
|
Diving depth operational, m |
300 |
During 2002 a proposed SSGN missile loadout included 21 TLAM IIIC cruise missiles with unitary warheads, 5 TLAM IIID1 cruise missiles with submunitions, 2 TLAM IIID2 cruise missiles with nonlethal magnetic pulse and graphite bomb warheads, 28 TTLAM cruise missiles with penetrator warheads, 24 TACMS-U ballistic missiles with 227kg HE warheads, 24 TACMS-A ballistic missiles with 300 M74 antipersonnel and antimaterial bomblets each, 18 TACMS-P ballistic missiles with Block III Earth Penetrator warheads, 18 TACMS-L ballistic missiles, each with 4 GPS-guided miniature autonomous cruise missiles, 4 SASST Search and Attack Specific Shape Targets, capable attack SCUD missiles, tanks and APCs. TACMS and SASST do not yet exist.
Naval service: No significant events.

Tennessee 2001

Ohio 2008
© Navypedia, 2016-20