
Puritan 1896
| No | Name | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comm | Fate |
| M1, 1920- BM1 | Puritan | 160 | John Roach, Chester // New York N Yd | 1875 | 6.12.1882 | 10.12.1896 | TS 1899-1902, receiving ship 6.1903 |
|
Displacement normal, t |
6060 |
|
Displacement full, t |
|
|
Length, m |
90.3 |
|
Breadth, m |
18.3 |
|
Draught, m |
5.49 mean |
|
No of shafts |
2 |
|
Machinery |
2 HCE, 8 cylindrical boilers |
|
Power, h. p. |
3700 |
|
Max speed, kts |
12.4 |
|
Fuel, t |
coal 410 |
| Endurance, nm(kts) | |
|
Armour, mm |
Harvey and nickel steel; belt: 356 - 152, deck: 51, barbettes: 356, turrets: 203, CT: 254 |
|
Armament |
2 x 2 - 305/35 Mk I, 6 x 1 - 102/40 Mk III/IV/V/VI, 6 x 1 - 57 Hotchkiss Mk I/II |
|
Complement |
200 |
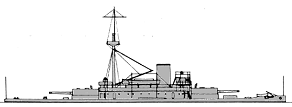
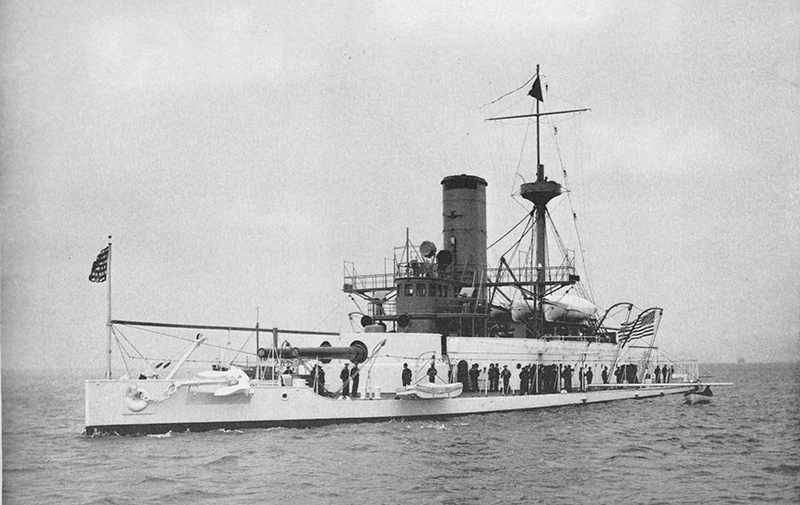
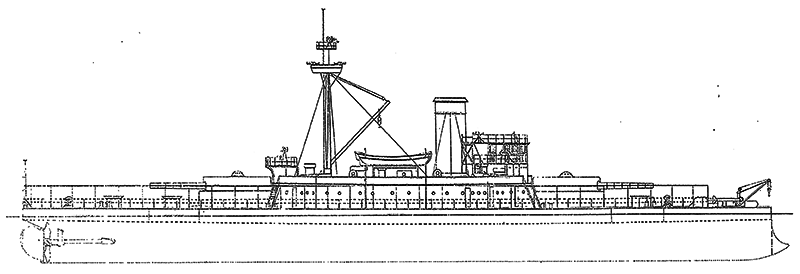
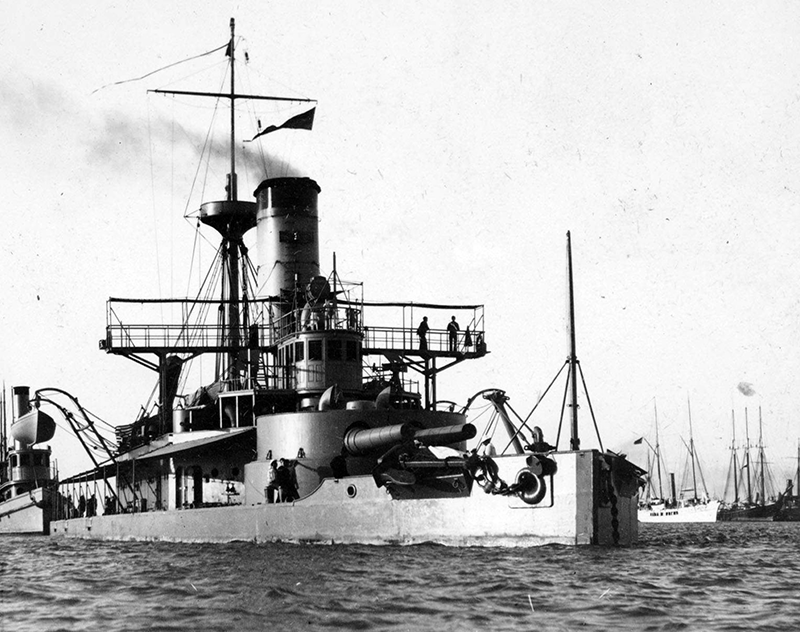
Project history: The largest of the 'New Navy' monitors, Puritan had no resemblance to the uncompleted Civil War ship of which she was nominally a repair. Her completion to the above design was authorized under the Act of 3.8.1886 and ordered 26.6.1889. She was heavily gunned and armoured and a powerful ship for her size, but except for coast defence her very low freeboard was a serious disadvantage. Puritan was iron-hulled.
Ship protection: Steel 51mm armour deck was connected with upper edge of iron main belt. The thickness of the belt was 356mm amidships and 152mm at ship ends. Barbettes had 356mm protection, turrets 203mm.
Modernizations: None.
Naval service: Puritan was used as TS at the Naval Academy in 1899-1902, as receiving ship at Philadelphia 6.1903-1904, as TS for Naval Militia in 1904-9/1909 and was finally decommissioned in April 1910. Since 1910 she was used as target ship Target B. In July, 1921 she was converted to radio controlled target ship IX6 and sold for BU in January 1922.
Puritan
Puritan
Puritan
© Navypedia, 2020