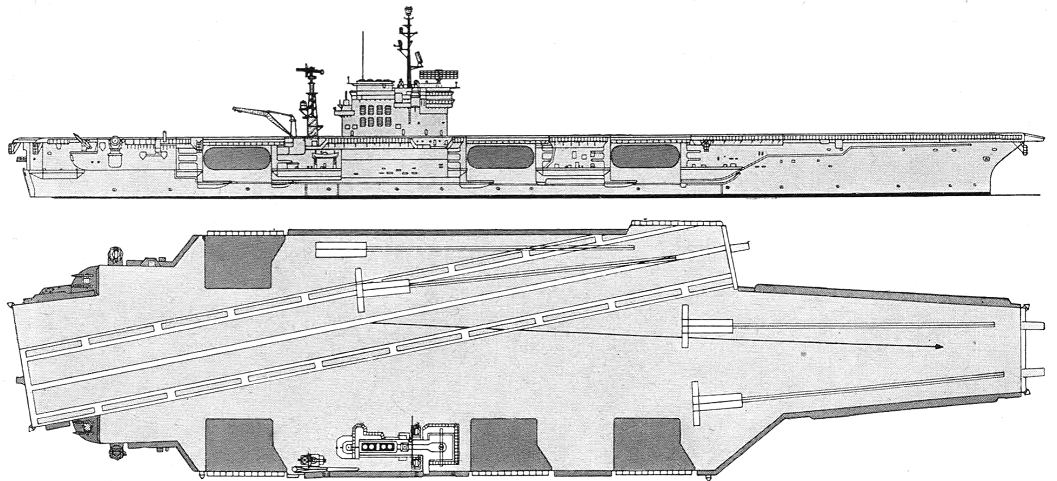

Kitty Hawk 1963
Kitty Hawk 1973
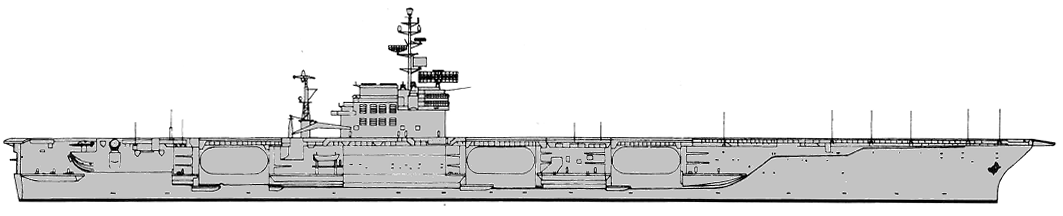
America 1977
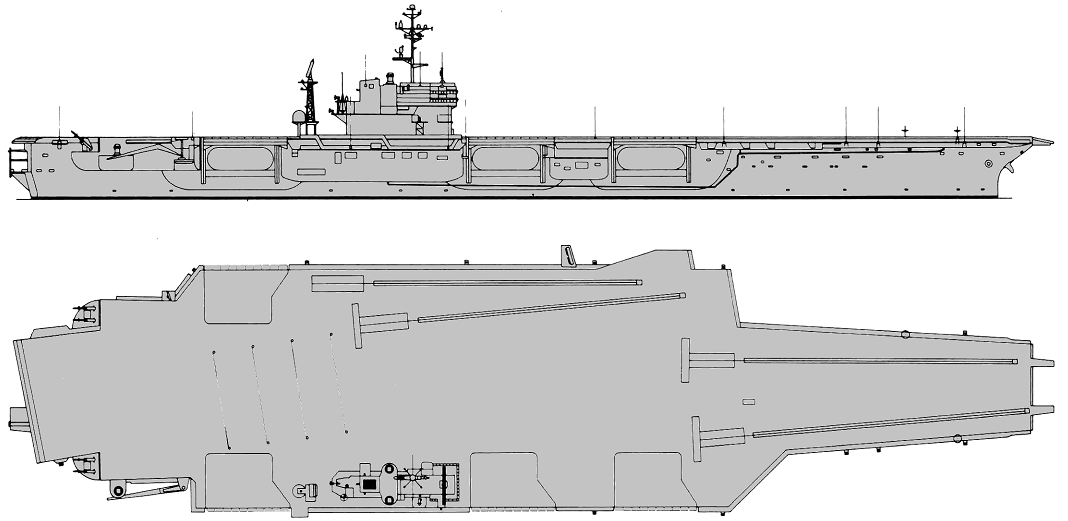
John F. Kennedy 1972
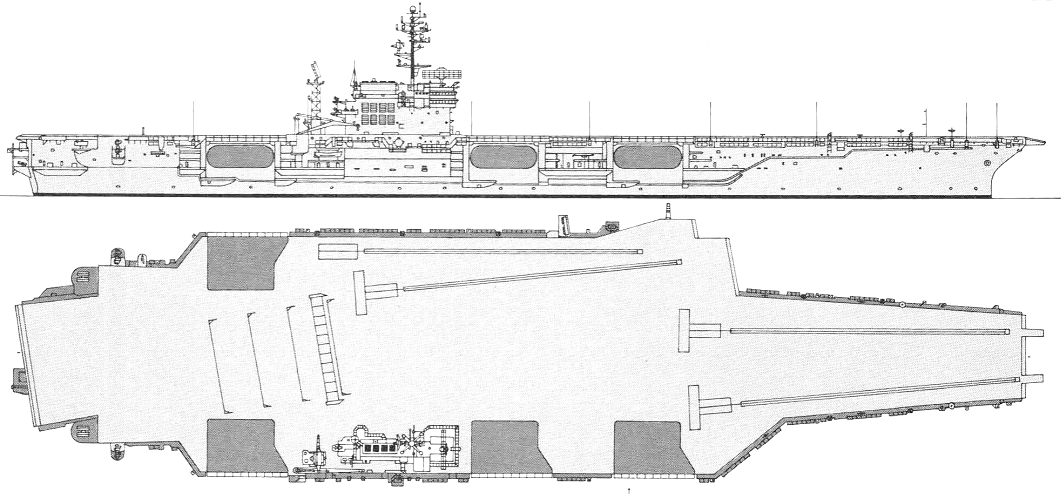
Kitty Hawk 1979
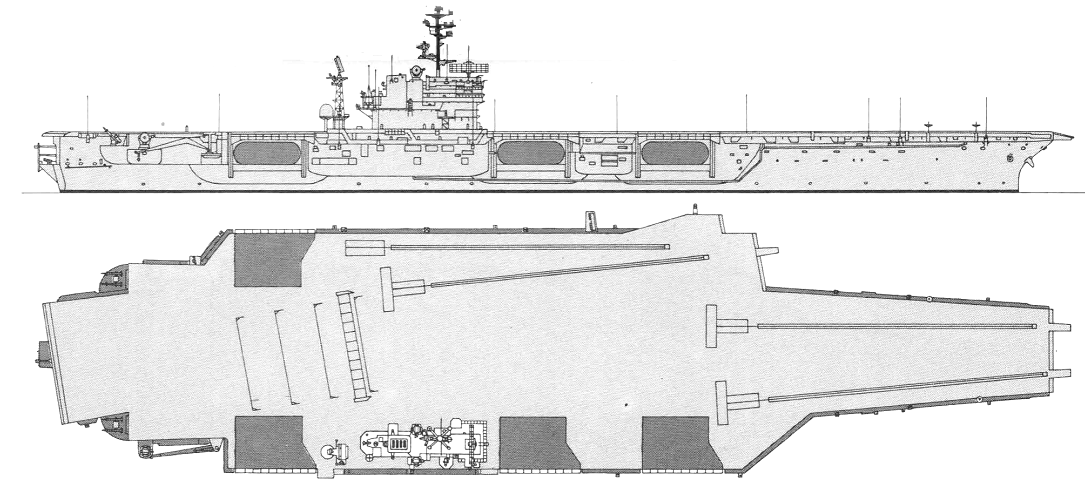
America 1979
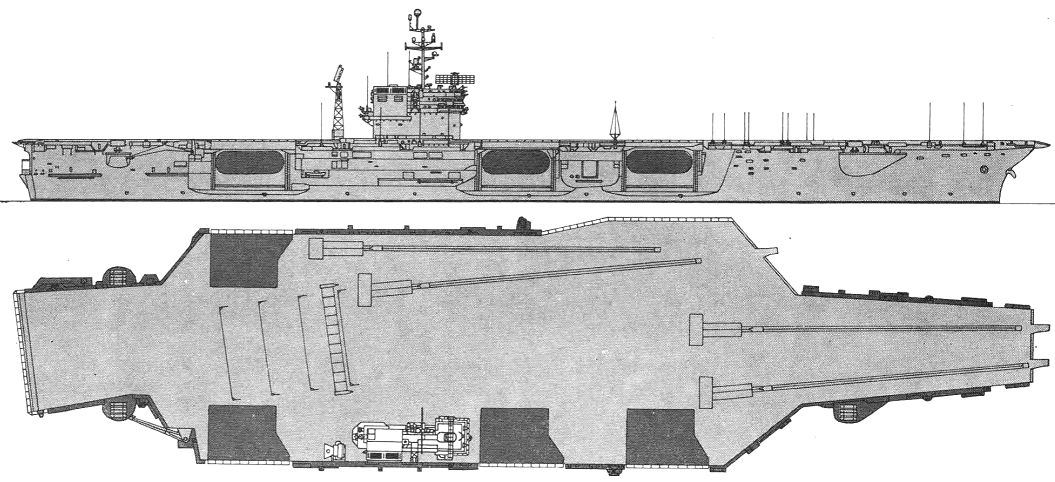
John F. Kennedy 1979
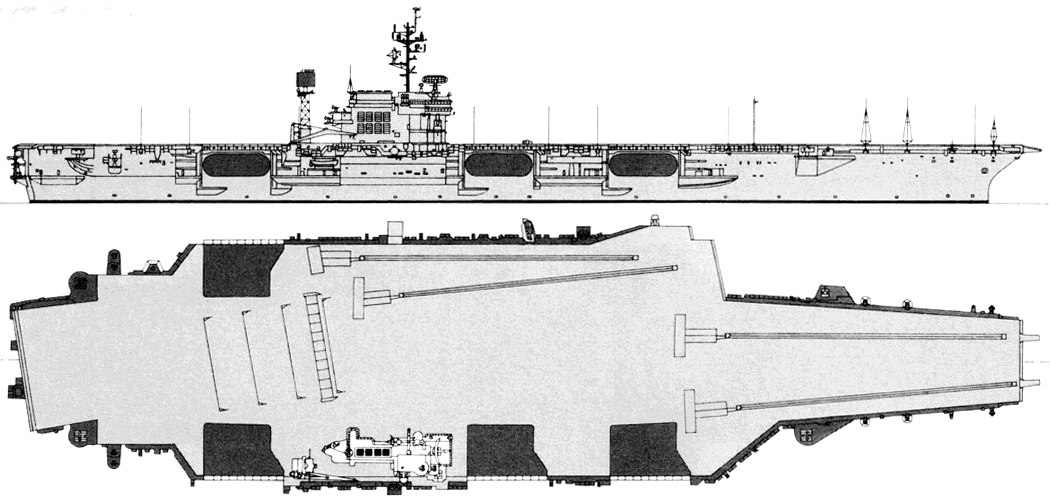
Constellation 1990
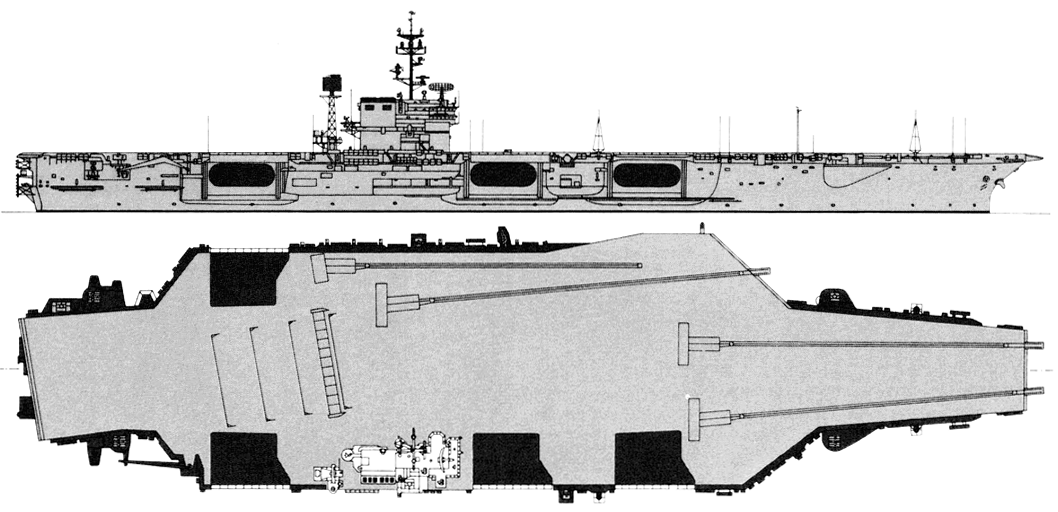
John F. Kennedy 1990
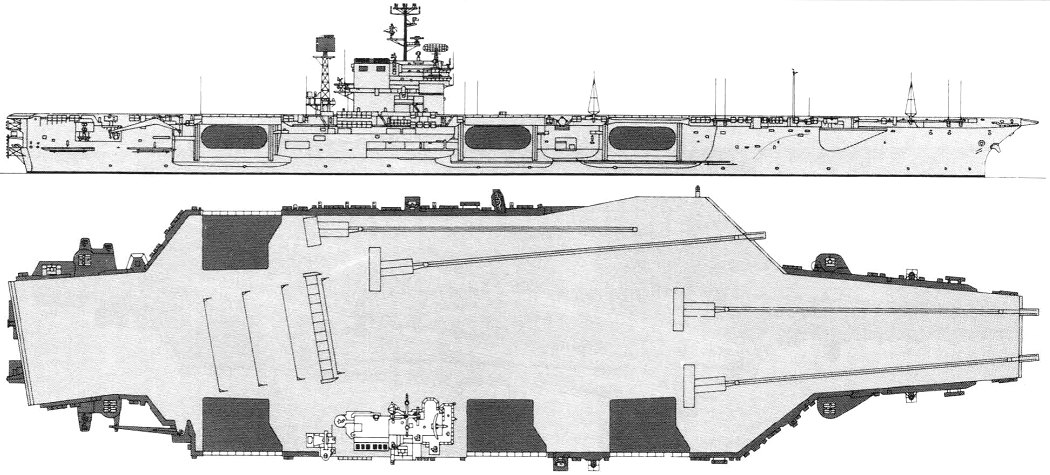
Constellation 2000
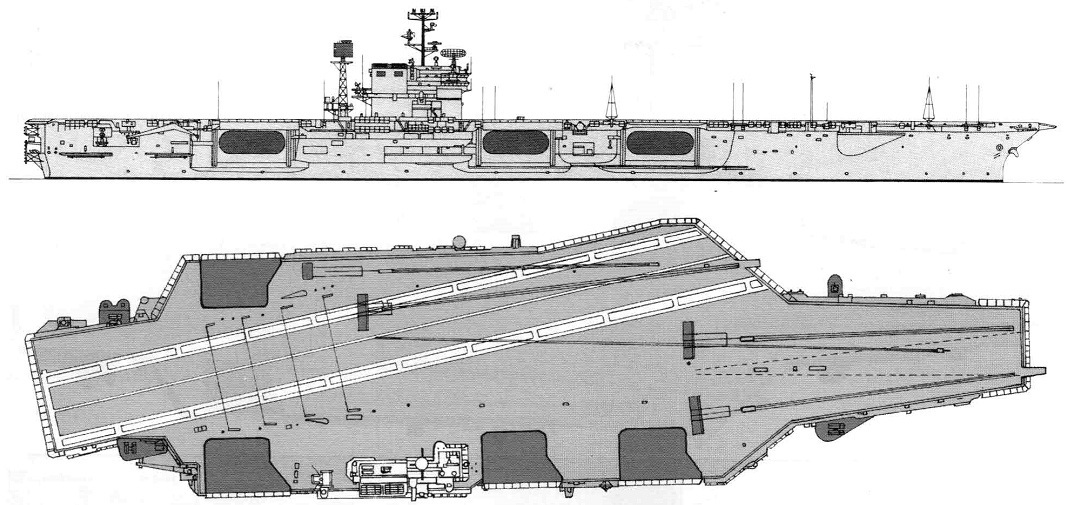
John F. Kennedy 2000
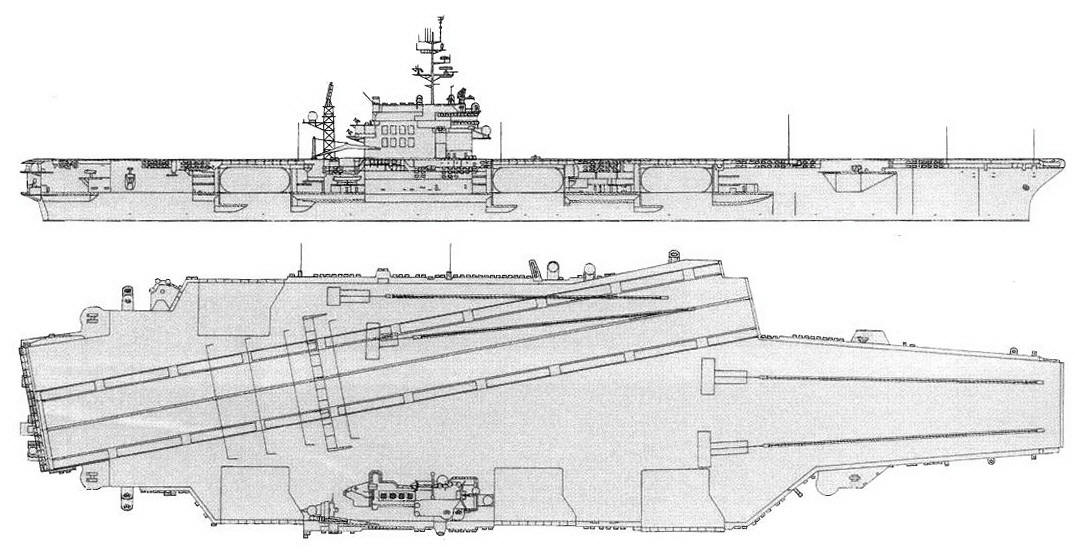
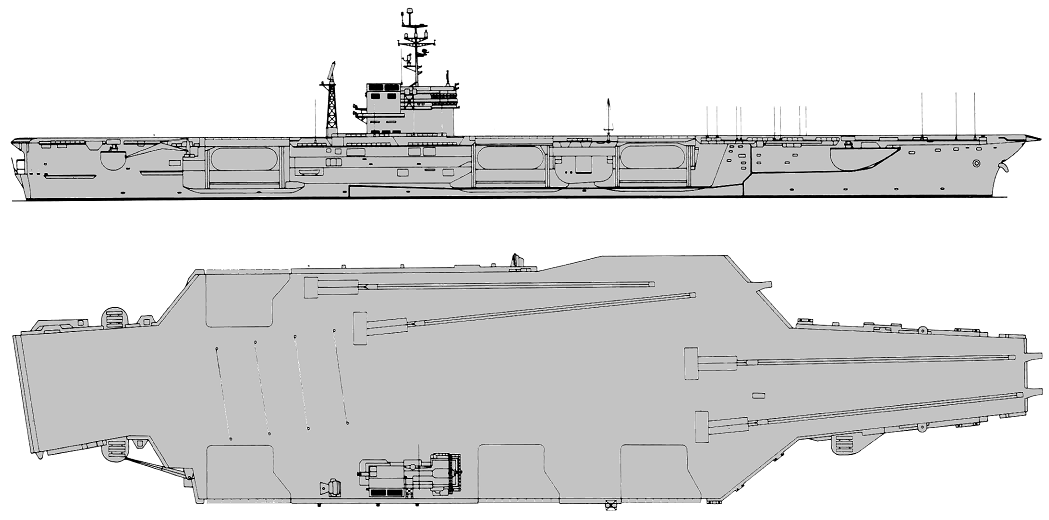
Kitty Hawk 2001
| No | Name | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comm | Fate |
| CVA63, 4.1973- CV63 | Kitty Hawk | 514 | New York SB, Camden | 27.12.1956 | 21.5.1960 | 29.4.1961 | stricken 10.2017 |
| CVA64, 6.1975- CV64 | Constellation | New York N Yd, Brooklyn | 14.9.1959 | 8.10.1960 | 27.10.1961 | stricken 12.2003 | |
| CVA66, 6.1975- CV66 | America | 561 | Newport News | 9.1.1961 | 1.2.1964 | 23.1.1965 | stricken 10.1998 |
| CVA67, 12.1974- CV67 | John F. Kennedy | 577 | Newport News | 22.10.1964 | 27.5.1967 | 7.9.1968 | stricken 10.2009 |
|
Displacement standard, t |
60005 |
|
Displacement full, t |
80945 |
|
Length, m |
301.8 wl 319.4 oa |
|
Breadth, m |
39.4 wl 76.7 ext |
|
Draught, m |
11.4 |
|
No of shafts |
4 |
|
Machinery |
4 sets Westinghouse geared steam turbines, 8 Foster Wheeler boilers |
|
Power, h. p. |
280000 |
|
Max speed, kts |
33.6 |
|
Fuel, t |
oil 7800 |
| Endurance, nm(kts) | 12000(20) |
|
Armour, mm |
CVA63, 64: belt summary: 150, flight deck: 45, gallery deck: 25, hangar deck: 37, main deck: 37, torpedo bulkhead: 76 CVA66, 67: belt summary: 135, flight deck: 45, hangar deck: 50, main deck: 56 |
|
Armament |
CVA63: 2 x 2 Terrier SAM (80 RIM-2), ~90 aircraft (FJ, F2H, F9F, F3H, F4D, F11F, F8U, F4H fighters, AD, A3D, A4D, A3J attackers, F2H-P, F9F-P, OE, A3D-P, F8U-P, F4H-P recon planes, AD-Q, F3D-Q, A3D-Q ECM planes, AD-W, WF EW planes, S2F ASW planes, TF cargo planes, HRS, HUP, HSS, HUS, HOK, HUK, HUL, HR2S helicopters) CVA64: 2 x 2 Terrier SAM (80 RIM-2), ~90 aircraft (FJ, F2H, F9F, F3H, F4D, F8U, F4H fighters, AD, A3D, A4D attackers, F2H-P, F9F-P, OE, A3D-P, F8U-P, F4H-P recon planes, AD-Q, F3D-Q, A3D-Q ECM planes, AD-W, WF EW planes, S2F ASW planes, TF cargo planes, HRS, HUP, HSS, HUS, HOK, HUK, HUL, HR2S, HSS-2 helicopters) CVA66: 2 x 2 Terrier SAM (80 RIM-2), ~90 aircraft (F-1, MF-1, F-2, F-9, F-8, F-4 fighters, A-1, AF-9, A-3, A-4, A-5, A-6 attackers, O-1, RA-3, RF-8, RF-4, RA-5 recon planes, EA-1, EF-10, EA-3, EA-6 ECM planes, EA-1, E-1, E-2 EW planes, S-2 ASW planes, KA-3 flying tankers, C-1 cargo planes, CH-19, SH-34, UH-34, HH-34, CH-34, OH-43, UH-43, UH-13, HH-13, CH-37, SH-3, CH-3, UH-2, HH-52, CH-46, UH-46, UH-1, HH-1 helicopters) CVA67: ~90 aircraft (F-9, F-8, F-4 fighters, AF-9, A-4, A-5, A-6, A-7 attackers, O-1, RF-8, RF-4, RA-5, OV-10 recon planes, EF-10, EA-3, EKA-3, ERA-3, EA-6 ECM planes, E-1, E-2 EW planes, S-2 ASW planes, KA-3 flying tankers, C-1, C-2 cargo planes, CH-19, SH-34, UH-34, HH-34, CH-34, UH-13, HH-13, SH-3, CH-3, UH-2, HH-52, CH-46, UH-46, UH-1, HH-1, CH-53 helicopters) |
| Sensors |
CVA63, 64: SPS-37A, SPS-39, SPS-8B, SPS-10F, SPN-10, SPN-12, SPN-35, 2x SPG-55 radars, WLR-1, ULQ-6 ECM suites CVA66: SPS-37A, SPS-39, SPS-30, SPS-43A, SPS-10F, SPN-10, SPN-12, SPN-35, 2x SPG-55 radars, SQS-23 sonar, WLR-1, WLR-3, WLR-11 ECM suites CVA67: SPS-37A, SPS-48E, SPS-43A, SPS-10F, SPN-10, SPN-12, SPN-35 radars, WLR-1, WLR-3, WLR-11 ECM suites |
|
Complement |
4685 |
Aircraft facilities (CV63, 64) (fd - 20,000 m², ha - 6,945 m² / 52,785 m³): Flight deck: 310.2 x 73.0m. Hangar: 225.5 x 30.8 x 7.60 m. There were 4 deck-edge elevators (40t, 21.4/25.9 x 15.9m). There were 4 C13 catapults. Aircraft fuel stowage: 353 500 l of petrol and 6 955 000 l of JP-5 jet fuel. Aviation ordnance stowage was 1800t.
(CV66, 67) (fd - 20,000 m², ha - 6,945 m² / 52,785 m³): Flight deck: 310.2 x 73.0m. Hangar: 225.5 x 30.8 x 7.60 m. There were 4 deck-edge elevators (40t, 21.4/25.9 x 15.9m). There were 3 C13 and 1 C13-1 catapults. Aircraft fuel stowage: 353 500 l of petrol and 6 955 000 l of JP-5 jet fuel. Aviation ordnance stowage was 1800t.
| Year | fighters | attackers | recon, EW, ECM | ASW and auxiliary | helicopters |
| 1964, Constellation | 24 F-4B, 12 F-8E | 24 A-4C, 10 A-3B, 12 A-1J/H | 4 RF-8G, 3 RA-3B, 3 EA-3B, 4 E-1B | - | 4 UH-2A |
| 1974, Constellation | 24 F-4J | 24 A-7C, 12 A-6A | 3 RA-5C, 4 EA-6B, 4 E-2C | 4 KA-6D, 10 S-3A | 8 SH-3H |
| 1988, John F. Kennedy | 24 F-14A | 24 A-6E | 5 EA-6B, 5 E-2C | 4 KA-6D, 10 S-3A | 8 SH-3H |
| 1991, America | 24 F-14A, 24 F/A-18A/B | 12 A-6E/KA-6D | 6 EA-6B, 4 E-2C | 8 S-3B | 8 SH-3H |
| 1993, America | 20 F-14A, 24 F/A-18A/B | 12 A-6E | 4 EA-6B, 4 E-2C | 4 KA-6D, 10 S-3B | 6 SH-3G/H |
| 1998, Constellation | 28 F-14A, 24 F/A-18C/D | 8 A-6E | 4 EA-6B, 4 E-2C | 4 KA-6D, 8 S-3A | 8 SH-3H |
| 1999, John F. Kennedy | 20 F-14A, 36 F/A-18 | --- | 4 EA-6B, 4 E-2C | 8 S-3A | 4 SH-60F |
| 2001, Kitty Hawk | 8 F/A-18A/C | 2 S-3B, 2 C-39B | 3 SH-60F, 20 MH-60 | ||
| 2003, Constellation | 10 F-14D, 36 F/A-18C | --- | 4 EA-6B, 4 E-2C | 8 S-3B | 6 SH-60F, 2 HH-60H |
| 2003, Kitty Hawk | 10 F-14A, 36 F/A-18C | --- | 4 EA-6B, 4 E-2C | 8 S-3B | 6 SH-60F, 2 HH-60H |
| 2003, John F. Kennedy | 20 F-14B, 24 F/A-18C | --- | 4 EA-6B, 4 E-2C | 8 S-3B | 6 SH-60F, 2 HH-60H |
| 2006, Kitty Hawk | 24 F/A-18E/F, 24 F/A-18A/C | 4 EA-6B, 4E-2C | 2 C-2A | 6 SH-60F/HH-60H | |
| 2006, John F. Kennedy | 24 F/A-18E/F, 24 F/A-18A/C | 4 EA-6B, 4E-2C | 2 C-2A | 6 SH-60F/HH-60H |
Project history: These ships actually formed three subclasses; all were improved Forrestals. An entirely new carrier design for CVA63 was foregone because of the imminence of the introduction of nuclear power, which, it was believed, would limit any new class to only two units. Kitty Hawk and Constellation differed from the Forrestals in having their islands moved aft, so that two instead of one elevator are forward of them, for improved flight deck operations. They also had a lattice radar mast aft of the island structure, and were armed with Terrier missiles (two twin Mk 10 launching systems on the port and starboard quarters, with paired SPG-55 guidance radars on the island structure). America (CVA 66) was very similar, having been built in preference to an austere nuclear carrier in FY61; she received updated Terrier, compatible with the Standard Missile. John F. Kennedy was built to a revised design, incorporating a new underwater protection system originally developed for the nuclear carriers, and, at first, without defensive weapons. Early in 1969 she was fitted with three Sea Sparrow launchers, and her three half-sisters were similarly refitted. Kennedy had her funnel angled to starboard.
America was the first attack carrier with a special integrated CIC/airborne ASW control centre (ASCAC) and, in 1981, retained SM-1 missiles and SPG-55B radar directors, as well as SPS-52 3-D radar instead of the more effective SPS-48 of her two sister-ships. America and John F. Kennedy were fitted for SQS-23 sonar in bow domes, on the theory that in a spread-out fleet formation it would be impossible to maintain a tight sonar screen, so that the carrier might have to detect submarines leaking through; SQS-23 was also fitted to some ASW carriers. Similar reasoning led to the installation of this sonar in Cleveland class missile cruisers. SQS-23 was not installed in CVA67 to reduce cost; presumably the measure lost much of its value as submarine weapon ranges increased beyond torpedo range.
Aviation ordnance and fuel capacity was slightly greater than that of the Forrestal class. Their rearranged flight decks made it far easier and safer to launch and recover aircraft simultaneously.
Ship protection (CV63, 64): Armour protection consisted of 4 protected decks (144mm summary) and distributed vertical armour (side armour and longitudinal bulkheads, 150mm summary). Also there was a box-shaped protection of magazines and vital zones. Underwater protection included 5 longitudinal bulkheads (4th bulkhead was 76mm-thick). Bottom was also protected.
(CV66): Armour protection consisted of 4 protected decks (151mm summary) and distributed vertical armour (side armour and longitudinal bulkheads, 135mm summary). Also there was a box-shaped protection of magazines and vital zones. Underwater protection included 5 longitudinal bulkheads (4th bulkhead was 76mm-thick). Bottom was also protected.
(CV67): Armour protection consisted of 4 protected decks (151mm summary) and distributed vertical armour (side armour and longitudinal bulkheads, 135mm summary). Also there was a box-shaped protection of magazines and vital zones. Underwater protection included 5 longitudinal bulkheads (4th bulkhead was 76mm-thick). Bottom was also protected.. Underwater protection was predecessor of underwater protection of Nimitz class.
Modernizations: 1960s, Kitty Hawk, Constellation: - ULQ-6 ECM suite; + WLR-3, WLR-11 ECM suites
early 1969, John F. Kennedy: + 3 x 8 Sea Sparrow SAM (24 RIM-7), 6x Mk 95, SPS-58 radars
early 1970s, Kitty Hawk, Constellation: - SPS-8B radar; + LN-66, SPS-43A radars
early 1970s, America: + LN-66 radar
late1970s, Kitty Hawk: - SPS-37A radar; + SPS-52, SPS-30 radars
late 1970s, America: - SPS-37A radar; + SPS-52 radar
late 1970s, John F. Kennedy: - SPS-37A radar; + SPS-49, LN-66 radars
1977, Kitty Hawk: - 2 x 2 Terrier SAM (80 RIM-2), 2x SPG-55 radars; + 2 x 8 Sea Sparrow SAM (16 RIM-7), 4x Mk 95, SPS-58 radars
1980, John F. Kennedy: + 3 x 6 - 20/76 Mk 15 Phalanx, 3x Mk 90 radars
1981, America: - 2 x 2 Terrier SAM (80 RIM-2), SQS-23 sonar; + 2 x 2 Standard SM-1MR SAM (80 RIM-66), 3 x 6 - 20/76 Mk 15 Phalanx, 3x Mk 90 radars
1982, America: - 2 x 2 Standard SM-1MR SAM (80 RIM-66), 2x SPG-55, SPS-52, SPS-30, SPS-39, SPS-43A, SPN-10, SPN-12 radars, WLR-1, WLR-3 ECM suites; + 3 x 8 Sea Sparrow SAM (24 RIM-7), 4x Mk 95, SPS-48C, SPS-49, SPN-41, 2x SPN-42, SPN-43A radars, WLR-1H, WLR-8, SLQ-17 ECM suites (forming SLQ-29 complex), 4x Mk 36 SRBOC decoy RL, NTDS CCS
1983, Kitty Hawk: - SPS-39, SPS-43A, SPS-52, SPS-30, SPS-58, SPN-10, SPN-12 radars, WLR-1, WLR-3 ECM suites; + 1 x 8 Sea Sparrow SAM (8 RIM-7), 3 x 6 - 20/76 Mk 15 Phalanx, SPS-48C, 3x Mk 90, SPN-41, 2x SPN-42, SPN-43A radars, WLR-1H, WLR-8, SLQ-17 ECM suites (forming SLQ-29 complex), 4x Mk 36 SRBOC decoy RL, NTDS CCS
2/1984, Constellation: - 2 x 2 Terrier SAM (80 RIM-2), SPS-37A, SPS-39, SPS-43A, 2x SPG-55, SPN-10, SPN-12 radars, WLR-1, WLR-3 ECM suites; + 3 x 8 Sea Sparrow SAM (24 RIM-7), 3 x 6 - 20/76 Mk 15 Phalanx, 4x Mk 95, SPS-48C, 3x Mk 90, SPN-41, 2x SPN-42, SPN-43A radars, WLR-1H, WLR-8, SLQ-17 ECM suites (forming SLQ-29 complex), 4x Mk 36 SRBOC decoy RL, NTDS CCS
10/1985, John F. Kennedy: - SPS-43A, SPS-58, SPN-10, SPN-12 radars; + 1 x 6 - 20/76 Mk 15 Phalanx, SPS-49, SPN-41, 2x SPN-42, SPN-43A, SPN-44, Mk 90, Mk 23 TAS radars, SLQ-26, SLQ-17 ECM suites, 4x Mk 36 SRBOC decoy RL, NTDS CCS
late 1980s, America: - SPS-58, SPS-48C, LN-66, SPS-49, SPS-10F, SPN-35, 2x SPN-42 radars, SLQ-29 (WLR-8, SLQ-17) ECM suite; + SPS-73, SPS-48E, SPS-64(v)9, SPS-67(v)1, SPS-49(v)5, Mk 23 TAS, 2x SPN-46 radars, SLQ-32(v)4 ECM suite, 4x Mk 36 SRBOC decoy RL, SLQ-25A Nixie torpedo decoy
2/1991, Kitty Hawk, early 1993, Constellation: - LN-66, SPS-10F, SPN-35, SPS-48C, 2x SPN-42 radars, SLQ-29 (WLR-8, SLQ-17) ECM suite; + SPS-73, SPS-48E, SPS-64(v)9, SPS-67(v)1, SPS-49(v)5, Mk 23 TAS, SPN-46 radars, SLQ-32(v)4 ECM suite, 4x Mk 36 SRBOC decoy RL, SLQ-25A Nixie torpedo decoy, NTDS CCS updated
9/1995, John F. Kennedy: - LN-66, SPS-10F, SPS-49, SPN-35, 2x SPN-42, SPN-43A radars, WLR-1, WLR-3, WLR-11, SLQ-26, SLQ-17 ECM suites; + SPS-73, SPS-64(v)9, SPS-67(v)1, SPS-49(v)5, SPN-43C, 2x SPN-46 radars, NTDS updated, SLQ-32(v)4 ECM suite, 4x Mk 36 SRBOC decoy launchers, SLQ-25A Nixie torpedo decoy
8/2001, Kitty Hawk: - 3 x 8 Sea Sparrow SAM, 4x Mk 95 radars; + 2 x 21 RAM SAM (42 RIM-116)
Naval service: No significant events.

Kitty Hawk 1978

John F. Kennedy

Kitty Hawk 2001
© Ivan Gogin, 2015-18