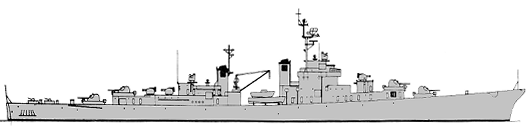

Norfolk 1954
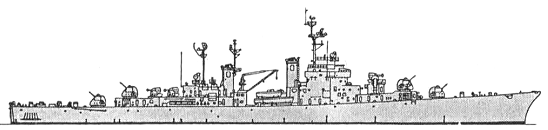
Norfolk 1959
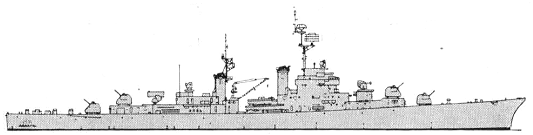
Norfolk 1970
| No | Name | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comm | Fate |
| DL1 | Norfolk | 488 | New York SB, Camden | 1.9.1949 | 29.12.1951 | 4.3.1953 | stricken 11.1973 |
| DL2 | New Haven | 489 | New York SB, Camden | --- | --- | --- | cancelled 9.1951 |
|
Displacement standard, t |
5556 |
|
Displacement full, t |
8315 |
|
Length, m |
158.5 wl 164.6 oa |
|
Breadth, m |
16.3 |
|
Draught, m |
5.80 |
|
No of shafts |
2 |
|
Machinery |
2 sets geared steam turbines, 4 Babcock & Wilcox boilers |
|
Power, h. p. |
80000 |
|
Max speed, kts |
33 |
|
Fuel, t |
oil 1230 |
|
Endurance, nm (kts) |
6000(20) |
|
Armament |
4 x 2 - 76/50 Mk 33, 4 x 2 - 20/70 Mk 24, 8 - 533 TT (beam, 30 Mk 17, Mk 35), 4 x 1 - 324 Mk 108 Weapon Alfa ASW rocket launchers |
|
Electronic equipment |
SPS-6, Mk 35, 2x SPG-48 radars, QHB, GHG (may be), QXB, SQG-1 sonars, 4x NAE torpedo decoy RL, FXR torpedo decoy |
|
Complement |
546 |
Project history: Laid down as an ASW cruiser (CLK). Norfolk was completed as the first of a new generation of large destroyers or 'destroyer leaders' (DL) or frigates (DL). She was designed specially as a counter to the new generation of Soviet submarines, which were expected to match the performance of the German Type XXI (and which materialized as the project 613). However, given her great size and high cost she could not be duplicated, and a projected sister-ship, CLK2, was never laid down. Hull design broadly followed that of the Atlanta class cruisers, and in details Norfolk reflected the experience of the Bikini nuclear tests. For example, special efforts were made to permit fallout to wash from her decks, and her bridgework was enclosed. ASW features included unusually large-diameter, slow-turning propellers for quietness, and her primary ASW weapon was the homing torpedo, fired from fixed tubes in her after superstructure. The visually more prominent Weapon Alfa (automatic rocket launcher) was a closer-range secondary battery. Even her anti-aircraft battery was experimental, four twin 76mm/70 having been specified. Ship had very wide specter of ASW sensors: QHB active/passive search, GHG passive array scanning sonar (planned, but correct information about installation is unknown), SQG-1 fire-control set and QXB search receiver.
In practice Norfolk was unique, serving with the Operational Test and Evaluation Force. She was test ship for ASROC and also for the SPS-26 electronically-scanned radar (the prototype of SPS-39). In 1959 conversion to a Terrier missile ship was proposed, as part of the same programme which produced the Mitscher and Forrest Sherman class missile destroyers (Tartar). Norfolk was dropped because of the high cost of conversion to what was perceived at the time as a relatively unreliable weapon, a consideration which curtailed the entire programme.
Modernizations: 1957: + SPS-26 radar
1959: - 4 x 2 - 76/50, 4 x 2 - 20/70, GHG, QHB, QXB sonars; + 4 x 2 - 76/70 Mk 37, SQS-4 sonar
1960: - 2 x 1 - 324 Mk 108 Weapon Alfa ASWRL; + 1 x 8 ASROC ASuR (8 RUR-5)
1962: - SQS-4 sonar; + SPS-37 radar, SQS-26 sonar
Naval service: No significant events.

Norfolk 1965
© Ivan Gogin, 2015