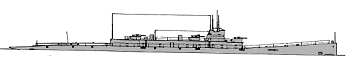

K26 1923
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
| K23 | Armstrong, Elswick | 1918 | --- | --- | cancelled 11.1918 | ||
| K24 | Armstrong, Elswick / Chatham DYd | 1918 | --- | --- | cancelled 11.1918 | ||
| K25 | Armstrong, Elswick / Chatham DYd | 1918 | --- | --- | cancelled 11.1918 | ||
| K26 | Vickers, Barrow / Chatham DYd | 1918 | 26.8.1919 | 6.1923 | sold 3.1931 | ||
| K27 | Vickers, Barrow | 1918 | --- | --- | cancelled 11.1918 | ||
| K28 | Vickers, Barrow / Chatham DYd | 1918 | --- | --- | cancelled 11.1918 |
|
Displacement standard, t |
|
|
Displacement normal, t |
2140 / 2530 |
|
Length, m |
107.0 |
|
Breadth, m |
8.50 |
|
Draught, m |
4.90 |
|
No of shafts |
2 |
|
Machinery |
2 sets Parsons geared steam turbines, 2 Yarrow boilers / 4 electric motors |
|
Power, h. p. |
10500 / 1440 |
|
Max speed, kts |
23.5 / 9.5 |
|
Fuel, t |
oil |
| Endurance, nm(kts) | 12500(10) / 30(4) |
|
Armament |
3 x 1 - 102/40 QF Mk IV, 6 - 533 TT (bow, 12), 4 - 450 TT (beam, 8) |
|
Complement |
59 |
| Diving depth operational, m | 50 |
Project history: In this class the known defects of the 'K' class were eliminated as far as possible. Motors, batteries and beam TT remained the same but a much heavier bow salvo of 6 533mm TT was provided. The bow was given more flare to improve seakeeping, and the superstructure was higher to protect funnels and uptakes. Other improvements were to extend the superstructure forward to form a gun platform and to move hydroplanes 4.9m further aft, where they were less susceptible to damage. Faster diving was possible by moving some ballast tanks to the internal hull, below the water line. Six were ordered early in 1918, but five were cancelled in November. The frames of K24, K25 and 28 were then ordered on 31 December 1918 to be taken to Chatham for completion, but that was later rescinded as well. In 1920 K26 was towed to Chatham and completed in June 1923.
Modernizations: 1929: - 4 - 450 TT (beam); + type 118 sonar
Naval service: No significant events.
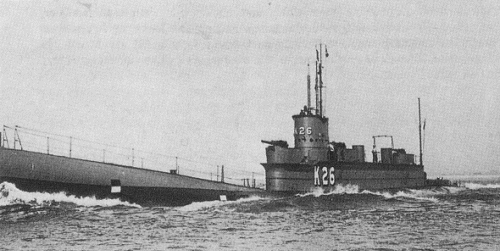
K26 1923
© Ivan Gogin, 2008-13