

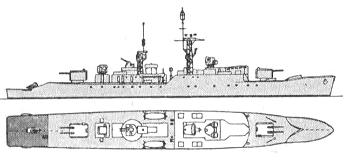
Puma 1957
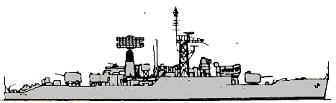
Leopard 1963
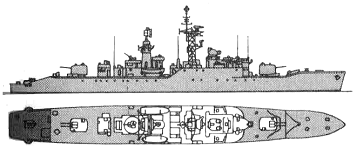
Leopard 1974
Lynx 1979
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
| Leopard | F14 | Portsmouth DYd | 25.3.1953 | 23.5.1955 | 30.9.1958 | BU 10.1977 | |
| Lynx | F27 | 679 | John Brown, Clydebank | 13.8.1953 | 12.1.1955 | 14.3.1957 | to Bangladesh 3.1982 (আবু বকর [Abu Bakr]) |
| Puma | F34 | 664 | Scotts, Greenock | 16.11.1953 | 30.6.1954 | 27.4.1957 | BU 12.1976 |
| Jaguar | F37 | 1476 | Denny, Dumbarton | 2.11.1953 | 20.7.1957 | 12.12.1959 | to Bangladesh 7.1978 (আলী হাইডের [Ali Haider]) |
|
Displacement standard, t |
2300 |
|
Displacement full, t |
2520 |
|
Length, m |
100.6 pp 103.6 oa |
|
Breadth, m |
12.2 |
|
Draught, m |
3.60 |
|
No of shafts |
2 |
|
Machinery |
8 ASR1 diesels |
|
Power, h. p. |
14400 |
|
Max speed, kts |
25 |
|
Fuel, t |
diesel oil 230 |
|
Endurance, nm(kts) |
7500(16) |
|
Armament |
F14, 27, 34: 2 x 2 - 120/45 Mk 6, 1 x 2 - 40/60 STAAG Mk 2, 1 x 3 - 305 Squid Mk 3 ASWRL F37: 2 x 2 - 120/45 Mk 6, 1 x 1 - 40/60 Mk 7, 1 x 3 - 305 Squid Mk 3 ASWRL |
|
Electronic equipment |
F14, 27, 34: type 275, type 960, type 293Q, type 974 radars, type 170, 174, 162 sonars F37: type 275, type 960, type 974, type 993 radars, type 170, 174, 162 sonars |
|
Complement |
205 |
Project history: For the remainder of the 1945 frigates it was decided to adopt diesel propulsion because it was felt that so many steam plants would overstretch the capacity of British industry. The Type 41 AA frigate was intended to support the Type 12, along with its half-sister, the Type 61 AD version, and the first orders were placed in August 1951. The 41/61 in steam form was the basic design and the 12 was developed from it. The raised forecastle of the Type 12 was adopted in order to enable speed to be kept up in a head sea, but was somewhat shorter and therefore lacking in elegance. Another unattractive feature was the absence of a funnel, for the diesel exhaust - trunking was brought up inside both lattice masts. This proved unsuccessful as well as unsightly, and to prevent the corrosion of masthead equipment Puma had her mainmast plated. The improvement was retro-fitted to the other ships.
By the standards of the day a most elaborate anti-aircraft defence was provided, with a Type 960 long-range air warning radar on the mainmast, a Mk 6M fire control system controlling two twin 114mm automatic mountings, backed up by a CRBF director aft, and a STAAG autonomous close-range 40mm mounting. The STAAG was not reliable, however; Jaguar entered service with a single 40mm gun in its place and the rest followed suit. Jaguar was the first to have the more effective Type 965 (AKE-1) long-range radar, but in time all four received it.
A fifth unit, Panther, was sold (before being laid down) to India as Brahmaputra; a replacement was ordered, but subsequently cancelled.
Modernizations: 1963, Leopard; 1964, Puma; 1966, Lynx: - 1 x 2 - 40/60, type 960, type 293Q radars; + 1 x 1 - 40/60 Mk 7, type 965 AKE-1, type 993 radars, UA-8/9 ECM suite
1967, Jaguar: - type 960 radar; + type 965 AKE-1 radar, UA-8/9 ECM suite
Naval service: No significant events.

Lynx 1977
Many thanks to Wolfgang Stöhr for additional information on this page.
© Ivan Gogin, 2015