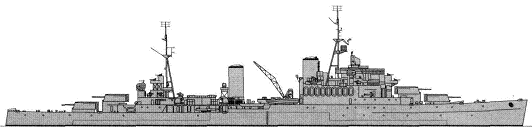

Gambia 1943
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
| 1st group | |||||||
| Fiji | 58 | 558 | John Brown, Clydebank | 30.3.1938 | 31.5.1939 | 17.5.1940 | sunk 22.5.1941 |
| Kenya | 14, 1948- C14 | 566 | A. Stephens, Linthouse | 18.6.1938 | 18.8.1939 | 27.9.1940 | stricken 9.1958 |
| Bermuda | 52, 1948- C52 | 568 | John Brown, Clydebank | 30.11.1939 | 11.9.1941 | 21.8.1942 | stricken 1962, sold for BU 8.1965 |
| Mauritius | 80, 1948- C80 | 1565 | Swan Hunter, Wallsend | 31.3.1938 | 19.7.1939 | 1.1.1941 | sold for BU 3.1965 |
| Gambia (RNZN 2.1944-3/1946) | 48, 1948- C48 | 1575 | Swan Hunter, Wallsend | 24.7.1939 | 30.11.1940 | 21.2.1942 | sold for BU 12.1968 |
| Jamaica | 44, 1948- C44 | 750 | Vickers-Armstrong, Barrow | 28.4.1939 | 16.11.1940 | 29.6.1942 | sold for BU 12.1960 |
| Nigeria | 60, 1948- C60 | 12 | Vickers-Armstrong, Tyne | 8.2.1938 | 18.7.1939 | 23.9.1940 | to India 4.1954 (Mysore) |
| Trinidad | 46 | Devonport DYd | 21.4.1938 | 21.3.1940 | 14.10.1941 | sunk 15.5.1942 | |
| 2nd group | |||||||
| Ceylon | 30, 1948- C30 | 569 | A. Stephens, Linthouse | 27.4.1939 | 30.7.1942 | 13.7.1943 | to Peru 12.1959 (Coronel Bolognesi) |
| Newfoundland | 59, 1948- C59 | 1589 | Swan Hunter, Wallsend | 9.11.1939 | 19.12.1941 | 20.1.1943 | to Peru 11.1959 (Almirante Grau) |
| Uganda, 14.1.1952 - Quebec (RCN 10.1944) | 66, 1948- C66, 1951- CCL31 | 17 | Vickers-Armstrong, Tyne | 20.7.1939 | 7.8.1941 | 3.1.1943 | to Canada 10.1944, stricken 6.1956 |
|
Displacement standard, t |
8530 |
|
Displacement full, t |
10450 (later 10830 - 11090) |
|
Length, m |
164.0 pp 169.3 oa |
|
Breadth, m |
18.9 |
|
Draught, m |
6.04 deep load (later 6.20 - 6.32) |
|
No of shafts |
4 |
|
Machinery |
4 sets Parsons steam geared turbines, 4 Admiralty 3-drum boilers |
|
Power, h. p. |
72500 |
|
Max speed, kn |
31.5 |
|
Fuel, t |
oil 1613 - 1700 |
| Endurance, nm(kts) | 10100(12) |
| Armour, mm |
belt: 89 - 83, bulkheads: 51 - 38, turrets: 51 - 25, barbettes: up to 25, deck: 51 - 32 |
|
Armament |
Fiji, Nigeria, Mauritius: 4 x 3 - 152/50 BL Mk XXIII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, 2 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 2 x 4 - 12.7/62, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, 2 aircraft (Walrus, Swordfish, Seafox), 1 catapult D-IV-H Kenya: 4 x 3 - 152/50 BL Mk XXIII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, 2 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 2 x 4 - 12.7/62, 2 x 3 - 533 TT Trinidad: 4 x 3 - 152/50 BL Mk XXIII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, 2 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 4 x 4 - 12.7/62, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, 2 aircraft (Walrus, Swordfish, Seafox), 1 catapult D-IV-H Jamaica: 4 x 3 - 152/50 BL Mk XXIII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, 2 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 4 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, 2 aircraft (Walrus, Swordfish, Seafox), 1 catapult D-IV-H Gambia: 4 x 3 - 152/50 BL Mk XXIII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, 2 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 2 x 1 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, 2 aircraft (Walrus, Swordfish, Seafox, Kingfisher), 1 catapult D-IV-H Bermuda: 4 x 3 - 152/50 BL Mk XXIII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, 2 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 10 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, 2 aircraft (Walrus, Swordfish, Seafox, Kingfisher), 1 catapult D-IV-H Uganda: 3 x 3 - 152/50 BL Mk XXIII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, 3 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 10 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, 2 aircraft (Walrus, Seafox, Kingfisher, Sea Otter, Seamew), 1 catapult D-IV-H Newfoundland: 3 x 3 - 152/50 BL Mk XXIII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, 3 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 8 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, 2 aircraft (Walrus, Seafox, Kingfisher, Sea Otter, Seamew), 1 catapult D-IV-H Ceylon: 3 x 3 - 152/50 BL Mk XXIII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 QF Mk XVI, 3 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 8 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, 2 x 3 - 533 TT |
|
Sensors |
Fiji, Kenya, Nigeria, Mauritius: type 279, type 281 radars Bermuda, Gambia, Jamaica, Trinidad: type 272, type 273, type 281, type 284, type 285 radars Uganda: type 272, type 281, type 284, type 285 radars Ceylon, Newfoundland: type 272, type 281, type 283, type 284, type 285 radars |
|
Complement |
730, 920 war |
Project history: Occurrence of Colony class became one of consequences of London conference in 1936, limited displacement of newly designed cruisers by 8000t. Design of Southampton class was revised under these requirements and result was more compact Fiji in which length of hull was by more than 10m shortened at the expense of cramped arrangement. Usage of less power machinery and lighter armour allowed to keep the same armament as on a prototype, and a transom stern has given the chance to avoid strong fall of speed (on 0.5kts). Waterline belt became a little thinner but at the expense of a smaller length of the hull reached end barbettes, and thickness of an armour deck even has increased. Return to more simple vertical funnels and masts became characteristic kind of these ships.
Small metacentric height was main lack of design and it has created serious problems at wartime modernizations: it was necessary to land one of main turrets for placing of numerous AA guns and the electronic equipment on most of class in the end of war. The last 3 ships of Fiji class (2nd group) were completed under some changed design considering experience of the first year of war: with the strengthened antiaircraft armament. Because of already mentioned very cramped arrangement one main turret had landed and catapult was removed (hangars have been left, but were used for other purposes).
Protection: Armoured belt extended from "A" to "Y" barbettes and to upper deck abreast boiler rooms and fore engine room and to main deck abreast aft engine room, CCC and magazines. Its thickness was 89 mm abreast magazines and 83 mm abreast machinery. Belt was closed by 51 - 38-mm bulkheads. Armoured deck was 51-mm thick (32-mm with 38-mm slopes over steering gear). Transom stern was 38-mm thick.
Modernizations: late 1940, Fiji: + 2 x 4 - 12.7/62, type 284 radar
8/1941, Kenya: + 2 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, 2 x 4 - 12.7/62, type 271 radar
11/1941, Nigeria: + 4 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, type 272, type 284 radars
12/1941, Kenya: - type 271 radar; + type 273, type 284 radars
2/1942, Gambia: + 6 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
3/1942, Mauritius: + 4 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, type 284, type 285 radars
5/1942, Trinidad: + 2 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
12/1942, Kenya: - 2 x 1 - 20/70, 4 x 4 - 12.7/62, type 279, type 281 radars; + 6 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, type 281B, type 282, type 285 radars
6/1943, Mauritius: - catapult with seaplanes, 2 x 4 - 12.7/62; + 20 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
9/1943, Nigeria: - 4 x 1 - 20/70, 2 x 4 - 12.7/62, type 272, type 279, type 281 radars; + 8 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, type 273, type 281B radars
9/1943, Gambia: - catapult with seaplanes, 2 x 1 - 40/39, 6 x 1 - 20/70; + 10 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, type 283 radar
9/1943, Jamaica: - catapult with seaplanes; + 6 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, 6 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
9/1943, Bermuda: + 6 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
11/1943, Newfoundland: - catapult with seaplane; + 2 x 4 - 40/56 Bofors Mk 1.2, 2 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, 2 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
12/1943, Kenya: + 2 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
1/1944, Nigeria: - catapult with seaplanes; + type 283 radar
4/1944, Ceylon: + 2 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, 8 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
5/1944, Mauritius: - type 279, type 281 radars; + type 273, type 281B radars
5/1944, Bermuda: - catapult with seaplanes, 12 x 1 - 20/70; + 8 x 2 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV
12/1944, Uganda: - 6 x 2 - 20/70, catapult with seaplanes, type 272, type 284 radars; + 2 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 4 x 1 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 8 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, type 274, type 277, type 293 radars
11/1944, Newfoundland: - type 272, type 281, type 284 radars; + type 274, type 277, type 281B, type 293 radars
4/1945, Kenya: - 1 x 3 - 152/50 ("X"); + 2 x 2 - 40/56 Bofors Mk VIII/IX
3/1945, Bermuda: - 1 x 3 - 152/50 ("X"), 4 x 2 - 20/70, type 272, type 281, type 284 radars; + 3 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 4 x 1 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, type 274, type 277, type 281B, type 293 radars
6/1945, Jamaica: - 1 x 3 - 152/50 ("X"), 4 x 2 - 20/70; + 3 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, 4 x 1 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII
6/1945, Uganda: - 4 x 2 - 20/70, type 272, type 281 radar; + 4 x 1 - 20/70 Oerlikon Mk II/IV, type 281B radar
8/1945, Kenya: - 8 x 2 - 20/70; + 3 x 2 - 40/56 Bofors Mk VIII/IX, 8 x 1 - 40/56 Bofors Mk III
8/1945, Bermuda: - 2 x 2 - 20/70, 2 x 1 - 20/70; + 4 x 1 - 40/56 Bofors Mk III
9/1945, Ceylon: - 4 x 2 - 20/70, 6 x 1 - 20/70; + 4 x 1 - 40/56 Bofors Mk III
8/1945, Mauritius: - 1 x 3 - 152/50 ("X"), type 273, type 281B, type 284 radars; + 3 x 4 - 40/39 2pdr QF Mk VIII, type 275, type 277, type 293, type 960 radars
late 1945, Jamaica: - 4 x 1 - 40/39; + 2 x 1 - 40/56 Bofors Mk III
10/1945, Nigeria: + 4 x 1 - 40/56 Bofors Mk III
1.1946, Bermuda: 3 x 3 - 152/50 Mk XXII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 Mk XIX, 4 x 1 - 40/60 Mk III, 5 x 4 - 40/39 Mk VII, 4 x 1 - 40/39 Mk VIII, 2 x 2 - 20/70 Mk V, 2 x 1 - 20/70 Mk III, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, type 273, type 274, type 277, type 281B, type 285, type 293 radars
3.1946, Gambia: 4 x 3 - 152/50 Mk XXII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 Mk XIX, 2 x 4 - 40/39 Mk VII, 10 x 2 - 20/70 Mk V, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, type 272, type 273, type 281, type 283, type 284, type 285 radars
1.1946, Jamaica: 3 x 3 - 152/50 Mk XXII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 Mk XIX, 2 x 1 - 40/60 Mk III, 5 x 4 - 40/39 Mk VII, 2 x 2 - 20/70 Mk V, 10 x 1 - 20/70 Mk III, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, type 272, type 273, type 281, type 284, type 285 radars
1.1946, Kenya: 3 x 3 - 152/50 Mk XXII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 Mk XIX, 5 x 2 - 40/60 RP.50 Mk V, 8 x 1 - 40/60 Mk III, 2 x 4 - 40/39 Mk VII, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, type 273, type 281B, type 282, type 284, type 285 radars
1.1946, Nigeria: 4 x 3 - 152/50 Mk XXII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 Mk XIX, 4 x 1 - 40/60 Mk III, 2 x 4 - 40/39 Mk VII, 8 x 2 - 20/70 Mk V, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, type 273, type 281B, type 283, type 284 radars
1.1946, Mauritius: 3 x 3 - 152/50 Mk XXII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 Mk XIX, 5 x 4 - 40/39 Mk VII, 24 x 1 - 20/70 Mk III, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, type 275, type 277, type 285, type 293, type 960 radars
1.1946, Ceylon: 3 x 3 - 152/50 Mk XXII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 Mk XIX, 4 x 1 - 40/60 Mk III, 3 x 4 - 40/39 Mk VII, 6 x 2 - 20/70 Mk V, 2 x 1 - 20/70 Mk III, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, type 272, type 281, type 283, type 284, type 285 radars
1.1946, Newfoundland: 3 x 3 - 152/50 Mk XXII, 4 x 2 - 102/45 Mk XIX, 2 x 4 - 40/60 Mk 2, 3 x 4 - 40/39 Mk VII, 10 x 2 - 20/70 Mk V, 2 x 1 - 20/70 Mk III, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, type 274, type 277, type 281B, type 283, type 285, type 293 radars
1954, Nigeria: - 1 x 3 - 152/50 ("X"); + 2x type 275 radars
1956, Newfoundland: + 2x type 275 radars
1956, Ceylon: + 2x type 262 radars
Naval service: Fiji was damaged 1.9.1940 by torpedo from German submarine U32 and was repaired for 6 months, she was again damaged 22.5.1941 off Crete coast by 3 direct hits and 1 near-miss of German air bombs (1 Bf 109 fghter and 1 Ju 88 bomber), abandoned, torpedoed by destroyer Matchless and sunk in 5 hours. Kenya was damaged by torpedo from Italian submarine Alagi 12.8.1942 and repaired till January, 1943. Nigeria was damaged by torpedo from talian submarine Axum 12.8.1942 and repaired till June, 1943. Trinidad was damaged by German air torpedo in Arctic 29.3.1942, temporarily repaired at Murmansk, again damaged by German bomb 15.5.1942 on way to Britain and was sunk by escort. Uganda was damaged by German FX1400 gliding bomb 13.9.1943 and repaired till October, 1944. Newfoundland was damaged by torpedo from Italian submarine Ascianghi 23.7.1943 and repaired till November, 1944.
Many thanks to Wolfgang Stöhr for additional information on this page.
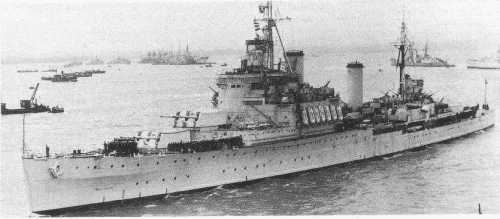
Kenya 1949

Ceylon 1946
© Ivan Gogin, 2008-15