
K-19 nuclear powered ballistic missile submarines (project 658) (1960 - 1962)

K-19 1960

K-19 1965

K-19 1979
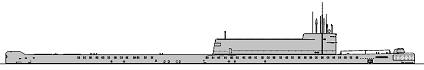
K-145 1976

K-178 1990
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
| К-19 [K-19], 7.1979- КС-19 [KS-19] | 901 | Northern Wks, Severodvinsk | 17.10.1958 | 11.10.1959 | 12.11.1960 | stricken 4.1990 | |
| К-33 [K-33], 7.1977- К-54 [K-54] | 902 | Northern Wks, Severodvinsk | 9.2.1959 | 6.8.1960 | 24.12.1960 | stricken 9.1987 | |
| К-55 [K-55] | 903 | Northern Wks, Severodvinsk | 5.8.1959 | 18.9.1960 | 27.12.1960 | stricken 3.1989 | |
| К-40 [K-40] | 904 | Northern Wks, Severodvinsk | 6.12.1959 | 18.6.1961 | 27.12.1961 | stricken 10.1986 | |
| К-16 [K-16] | 905 | Northern Wks, Severodvinsk | 5.5.1960 | 31.7.1961 | 28.12.1961 | stricken 3.1989 | |
| К-145 [K-145] | 906 | Northern Wks, Severodvinsk | 21.1.1961 | 30.5.1962 | 28.10.1962 | stricken 3.1989 | |
| К-149 [K-149], 1969- К-149 Украинский комсомолец [K-149 Ukrainskiy Komsomolets], 3.1990- КС-149 Украинский комсомолец [KS-149 Ukrainskiy Komsomolets], 6.1992- БС-149 [BS-149] | 907 | Northern Wks, Severodvinsk | 12.4.1961 | 20.7.1962 | 27.10.1962 | stricken 11.1995 | |
| К-178 [K-178] | 908 | Northern Wks, Severodvinsk | 11.9.1961 | 23.9.1962 | 8.12.1962 | stricken 4.1990 |
|
Displacement standard, t |
|
|
Displacement normal, t |
4080 / 5345 |
|
Length, m |
114.1 |
|
Breadth, m |
9.20 |
|
Draught, m |
7.68 |
|
No of shafts |
2 |
|
Machinery |
2 VM-A nuclear reactors, 2 GTZA-601 geared steam turbines units |
|
Power, h. p. |
35000 |
|
Max speed, kts |
18 / 26 |
|
Fuel, t |
nuclear |
|
Endurance, nm(kts) |
practically unlimited |
|
Armament |
3 R-13 SLBM (3 4K50), 4 - 533 TT (bow, 4), 4 - 400 TT (2 bow, 2 stern, 12) |
|
Electronic equipment |
RLK-101 Albatros radar, MG-200 Arktika or Arktika-M, MG-10 Kola sonars, Nakat ECM suite |
|
Complement |
104 |
|
Diving depth operational, m |
240 |
Project history: This design was a ballistic-missile equivalent of Project 627; note that the hull-numbers of the two classes are interleaved. Like the contemporary Project 629, this class was modified to fire R-21 (Project 658M). Unlike Project 629, this type had the new 40cm anti-escort defensive torpedo (MGT).
Modernizations: 1963, K-19; 1964, K-33; 1966, K-149; 1968, K-40, K-55, K-178; 1971, K-16 - under Project 658M: - 3 R-13 SLBM; + 3 R-21 SLBM (3 4K55), Plutoniy sonar; 4030/5000t, 7.30m draught, compl. 128
1976, K-145 - under Project 701: was lengthened, 4971/6400t, 129.8x9.20x8.20m, 15/23.3kts, compl. 123; armament consisted of 6 R-29 SLBM (6 4K75), 4 - 533 TT (bow, 4), 4 - 400 TT (2 bow, 2 stern, 8), sensors were RLK-101 Albatros radar, MG-200 Arktika-M, Plutoniy sonars, Nakat ECM suite, Alfa-701 CCS
late 1970s, all 658M: - 3 R-21 SLBM; + 3 R-21M SLBM
1979, K-19 - under Project 658S: - 3 R-21M SLBM
1983, K-55; 1984, K-178 - under Project 658U: - 3 R-21M SLBM
1985, K-16: - 3 R-21M SLBM; + wake detector
Naval service: K-19, the lead ship, had a particularly unfortunate reputation in the Soviet Navy; she was nicknamed 'Hiroshima'. On 4 July 1961 she lost pressure in her primary coolant loop, causing ten radiation deaths, she had to be towed back to base. She collided with USN submarine Gato 15 November 1969 at the entrance to the White Sea. In another accident, 24 February 1972, twenty-nine men died.
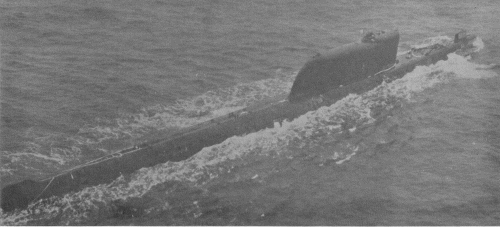
Project 658M 1978
© Ivan Gogin, 2015