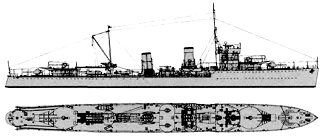

Evertsen 1936
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
| De Ruyter, 1933- Van Ghent | DR, 1933- GT | 179 | De Schelde, Vlissingen | 8.1925 | 23.10.1926 | 5.1928 | wrecked 15.2.1942 |
| Evertsen | EV | Burgerhout`s, Rotterdam | 8.1925 | 29.12.1926 | 5.1928 | lost 28.2.1942 | |
| Kortenaer | KN | Burgerhout`s, Rotterdam | 8.1925 | 30.7.1927 | 9.1928 | sunk 27.2.1942 | |
| Piet Hein | PH | Burgerhout`s, Rotterdam | 8.1925 | 2.4.1927 | 1.1928 | sunk 19.2.1942 |
|
Displacement standard, t |
1316 |
|
Displacement full, t |
1640 |
|
Length, m |
93.6 pp 98.2 oa |
|
Breadth, m |
9.53 |
|
Draught, m |
2.97 |
|
No of shafts |
2 |
|
Machinery |
2 sets Parsons geared steam turbines, 3 Yarrow boilers |
|
Power, h. p. |
31000 |
|
Max speed, kts |
36 |
|
Fuel, t |
oil 300 |
|
Endurance, nm(kts) |
3200(15) |
|
Armament |
4 x 1 - 120/50 Bofors No.4, 2 x 1 - 75/52 SA No.2, 4 x 1 - 12.7/90, 2 x 3 - 533 TT, 4 DCT (12), 32 mines, 1 seaplane (C.VIIW) |
|
Complement |
129 |
Project history: In the early twenties Dutch Navy has started replacement of obsolete destroyers of "Roofdier" (Fret) class, built prior to beginning of the First World War. The design was developed by Yarrow and was based on a construction of British destroyer Ambuscade, but was adapted for building by Dutch shipbuilders. Four destroyers were laid down by summer of 1925. They received names in honour of Dutch naval commanders, therefore they are quite often called as 1st series of "Admiralen" type.
Outwardly ships did not differ from British analogues, but there were numerous changes in details. Main calibre consisted of Bofors No.4 120mm/50 guns which placed in single mounts on two fore and aft. Guns No.2 and No.3 had no shields, and No.1 and No.4 were covered only in front. For a fire control two rangefinders were available: one over the bridge, and second on portside of platform between TTs. To increase offensive potential of destroyers, they had mine rails.
Seaplane carrying ability was necessary, according to Dutch Naval commanders, for service in waters of the Dutch East Indies, and was the most unusual detail of the design. Seaplane should be stored over the second TT bank on light platform on which it should be handled by a derrick placing near to a mainmast. In turn, mainmast should be transferred from aft superstructure to platfrom between TTs, and two searchlights have been placed on the platforms abreast fore funnel. Standard seaplane in a beginning of war was Fokker C.VIIW, single-engined double-seat biplane, armed with MGs and capable to carry some small bombs, however to the beginning of operations on Pacific destroyers have landed their aviation equipment.
Modernizations: 1940-1941, all: - seaplane
1941, Van Ghent: + type 128 sonar
Naval service: De Ruyter was renamed Van Ghent in 1933 to free a name to new cruiser. Van Ghent was hard damaged 15.2.1942 as result of wrecking to a reef at Tjillajap, abandoned and sunk by gunfire of destroyer Banckert. Piet Hein was sunk 19.2.1942 by Japanese destroyers Asashio, Oshio and Michishio in Badoeng Strait. Kortenaer was sunk 27.2.1942 by torpedo hit from Japanese cruiser Haguro in Java sea. Evertsen was hard damaged 28.2.1942 in battle against Japanese destroyers Shirakumo and Murakumo in Sunda Strait, ran aground and 1.3.1942 was blown up by crew.

Evertsen
Many thanks to Wolfgang Stöhr for additional information on this page.
© Ivan Gogin, 2011-14