HA62 1944
|
Names |
B: 波53 [HA53] C: 波62 - 76 [HA62 - 76] |
|
Builders |
Ourazaki, Kure: HA53, 62 - 76 |
|
Commissioned |
1943: HA53 1944: HA62 - 76 |
|
Losses |
8 boats of "C" class (1944 - 1945) |
|
Transfers |
none |
| Discarding | all survived: surrendered 8.1945 and BU |
|
Displacement standard, t |
|
|
Displacement normal, t |
49 |
|
Length, m |
24.9 |
|
Breadth, m |
1.88 |
|
Draught, m |
1.88 |
|
No of shafts |
1 |
|
Machinery |
1 diesel-generator / 1 electric motor |
|
Power, h. p. |
40 / 600 |
|
Max speed, kts |
6.5 / 18.5 |
|
Fuel, t |
0.5 |
| Endurance, nm(kts) | 350(6.5) / 120(4) |
| Armament |
2 - 450 TT (bow, 2) |
|
Complement |
3 |
|
Diving depth operational, m |
Project history: Works on midget submarines have begun in Japan in 1933. According to Naval Staff plans midget submarines were supposed to use for attack of enemy bases and anchorages. To a site of operation they should be carried by specialised carrier submarines. In the conditions of the strict privacy two experimental midgets were built in 1934. For concealment of true assignment of boats they were officially classified as "target submarines" (A-Hyoteki). On results of trials in the project necessary improvements were brought, then serial building of midget submarines under designation Ko-Hyoteki has been developed. As carriers seaplane carriers Chiyoda and Chitose and Hei-Gata (C) type submarines were arranged.
At designing the basic thrust became on achievement of a high submerged speed. For this purpose submarines received powerful (for so small ship) electric motor, and hull have given streamlined spindle-shaped form. This combination has ensured to first Ko-Hyoteki submarines 23kts submerged speed (subsequent boats because of the brought changes reached 18-19kts). Two 450mm TTs placed in a bow one over another were basic weapon.
First midget submarines possessed the scanty endurance defined in capacity of accumulators: boats had no generators, and battery recharge was possible only onboard of carrier or on base. From elimination of this lack, designing of an improved version (B type) has begun in autumn 1942, in which operating experience of A type has been considered. In early 1943 improved submarine ÍA53 has passed trials then a series of practically of the same type boats of C type was built. Main difference from A type consisted in occurrence of diesel-generator for battery recharging (full recharge held 18 hours).
As carriers for B and C types boats landing ships of Ò1 class were used.
Modernizations: None.
Naval service: Unfortunately, the information about fates of Japanese midget submarines had scrappy and frequently inconsistent character. It is known, that in 1944-1945 during defence of Philippines and Okinawa 8 boats of C type were lost.
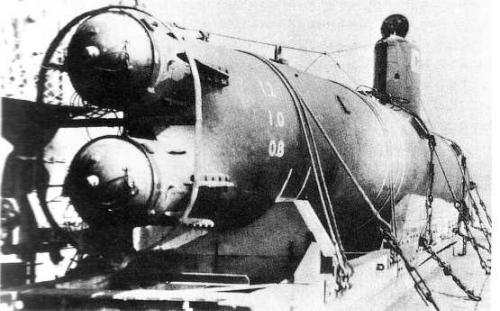
HA69 on board of landing ship 5-go 8.1944
© Ivan Gogin, 2008-14