U73 1940

U47 1942
U84 1943
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
| U45 | 580 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 2.1937 | 27.4.1938 | 6/1938 | sunk 14.10.1939 | |
| U46 | 581 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 2.1937 | 10.9.1938 | 11/1938 | scuttled 4.5.1945 | |
| U47 | 582 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 2.1937 | 29.10.1938 | 12/1938 | lost 8.3.1941 | |
| U48 | 583 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 11.1938 | 8.3.1939 | 4/1939 | scuttled 3.5.1945 | |
| U49 | 584 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 9.1938 | 24.6.1939 | 8/1939 | sunk 15.4.1940 | |
| U50 | 585 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 11.1938 | 1.11.1939 | 12/1939 | sunk 6.4.1940 | |
| U51 | 586 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 2.1937 | 11.6.1938 | 8/1938 | sunk 20.8.1940 | |
| U52 | 587 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 3.1937 | 21.12.1938 | 2/1939 | sunk 3.5.1945 | |
| U53 | 588 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 3.1937 | 6.5.1939 | 6/1939 | sunk 23.2.1940 | |
| U54 | 589 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 9.1938 | 15.8.1939 | 9/1939 | sunk 23.2.1940 | |
| U55 | 590 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 11.1938 | 11.10.1939 | 11/1939 | sunk 30.1.1940 | |
| U73 | 1 | Vulcan, Vegesack | 11.1939 | 27.7.1940 | 9/1940 | sunk 16.12.1943 | |
| U74 | 2 | Vulcan, Vegesack | 11.1939 | 31.8.1940 | 10/1940 | sunk 2.5.1942 | |
| U75 | 3 | Vulcan, Vegesack | 12.1939 | 18.10.1940 | 12/1940 | sunk 28.12.1941 | |
| U76 | 4 | Vulcan, Vegesack | 12.1939 | 3.10.1940 | 12/1940 | sunk 5.4.1941 | |
| U83 | 291 | Flenderwerft, Lübeck | 10.1939 | 9.12.1940 | 2/1941 | sunk 9.3.1943 | |
| U84 | 280 | Flenderwerft, Lübeck | 11.1939 | 27.2.1941 | 4/1941 | lost 7.8.1943 | |
| U85 | 281 | Flenderwerft, Lübeck | 12.1939 | 10.4.1941 | 6/1941 | sunk 14.4.1942 | |
| U86 | 282 | Flenderwerft, Lübeck | 1.1940 | 10.5.1941 | 7/1941 | lost 29.11.1943 | |
| U87 | 283 | Flenderwerft, Lübeck | 4.1940 | 21.6.1941 | 8/1941 | sunk 4.3.1943 | |
| U99 | 593 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 3.1939 | 12.3.1940 | 4.1940 | sunk 17.3.1941 | |
| U100 | 594 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 5.1939 | 10.4.1940 | 5.1940 | sunk 17.3.1941 | |
| U101 | 595 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 3.1939 | 13.1.1940 | 3.1940 | sunk 3.5.1945 | |
| U102 | 596 | Germaniawerft, Bremen | 5.1939 | 21.3.1940 | 4.1940 | sunk 1.7.1940 |
|
Displacement standard, t |
|
|
Displacement normal, t |
753 / 1040 |
|
Length, m |
66.5 |
|
Breadth, m |
6.20 |
|
Draught, m |
4.74 |
|
No of shafts |
2 |
|
Machinery |
U45, 46, 49, 99, 100: 2 Germania diesels / 2 BBC electric motors U47, 48, 50, 83, 84, 87, 102: 2 Germania diesels / 2 AEG electric motors U51, 52, 54, 73 - 76, 85, 86: 2 MAN diesels / 2 BBC electric motors U53, 55, 101: 2 MAN diesels / 2 AEG electric motors |
|
Power, h. p. |
2800 - 3200 / 750 |
|
Max speed, kts |
17.2 - 17.9 / 8 |
|
Fuel, t |
diesel oil 100 - 108 |
| Endurance, nm(kts) | 8700(10) / 90(4) |
|
Armament |
1 x 1 - 88/42 SK C/35, 1 x 1 - 20/65 C/38, 5 - 533 TT (4 bow, 1 stern, 14 or 39 mines) U83: 1 x 1 - 88/42 SK C/35, 1 x 1 - 20/65 C/38, 4 - 533 TT (bow, 12 or 36 mines) |
| Electronic equipment | GHG hydrophone |
|
Complement |
44 |
| Diving depth operational, m | 100 |
Project history: Submarines of VII series became the most known submarines of the Second World War and the most numerous submarines in history. They were presented Kriegsmarine chiefs as practically ideal submarine type, combining strong armament for her displacement, excellent manoeuvring capabilities, very small diving time (25-20sec), considerable endurance and relative cheapness of building.
Design was projected on the basis of coastal submarine of UB-III type of of the First World War, but with usage of lines plan of of II series submarine, which dimensions have been increased by linear conversion. Single-hulled, with adding of saddle tanks for improvement of a surfaced buoyancy and internal arrangement of fuel tanks. Pressure hull thickness reached 18.5mm, that ensured a working diving depth 100m and maximal 200m.
From VIIB series a vertical rudder was replaced by double and fuel stowage was increased, for what the hull was lengthened on 2m and part of saddle tanks were converted for fuel stowage. Stern TT was installed in a pressure hull and placed between rudders, 20mm MG was transferred from deck to CT. The weak ventilating system was considered as one of few lacks of the design, but during war majority of submarines were arranged with the additional vent pipes which were passing outside of the CT.
Instead of torpedoes submarines could carry 24 TMA or 36 TMB mines. In connection with lagging of armament production one boat (U83) had no stern TT.
In the end 1942 decision to remove 88mm gun from all boats of VII series was accepted, but part from them, especially training and operating on minor theatres, have stored it till the end of war. Since summer of 1942 strengthening of AA armament was begun. Aft from a fin structure the low-level platform (so-called "Wintergarten") with 1 twin, then 1 quadruple 20mm MG mount was mounted; behind the bridge there were 2 single or twin 20mm MGs. Submarines, served on Mediterranean, received often Italian twin 13.2mm MGs. From early 1944 boats began to be equipped by a snorkel (the first was U264).
Order for the first 6 submarines of VIIA series has been given out 1.4.1935; on last boats of VIIC/42 series 17.4.1943, but because of the exclusion of Kriegsmarine staff for a laying of new submarines of VII series their building did not begin.
Modernizations: late 1942, most survived: - 1 x 1 - 88/42; + 1 x 2 - 20/65 C/38, 1 x 1 - 20/65 C/38, FuMO 30 radar, FuMB 1 Metox ECM suite
1943-1944, most survived: - FuMB 1 Metox ECM suite; + FuMB 3 Bali, FuMB 6 Palau ECM suites
1944-1945, some survived: - FuMO 30 radar; + FuMO 61 radar
1944 - 1945, most survived: - 2 x 1 - 20/65; + 1 x 1 - 37/69 FlaK M/42, 1 x 2 - 20/65 C/38.
Naval service: In operations 437 submarines of VII series were lost.
U45 was sunk 14.10.1939 by British destroyers Inglefield, Icarus, Intrepid and Ivanhoe SW off Ireland. U47 after 7.3.1941 was lost in Northern Atlantic S off Iceland by unknown cause. U49 was sunk 15.4.1940 by British destroyers Fearless and Brazen in Vogs-fjord, Norway. U50 was lost, possibly, 6.4.1940 N off Terschelling on mines laid by British destroyers Esk, Express, Icarus and Impulsive.
U51 was torpedoed 20.8.1940 by British submarine Cachalot W off St. Nazaire. U52 was sunk 3.5.1945 by British Typhoons of 175th RAF sqn at Neustadt. U53 was sunk 23.2.1940 by British destroyer Gurkha W off Shetland. U54 was lost, possibly, 13.2.1940 N off Terschelling on mines laid by British destroyers Ivanhoe and Intrepid. U55 was sunk 30.1.1940 by British destroyer Whitshed, sloop Fowey and Sunderland of 228th RAF sqn SW off Scilly. U73 was sunk 16.12.1943 by American destroyers Woolsey and Òriððå N off Oran. U74 was sunk 2.5.1942 by British destroyers Wishart and Wrestler and Catalina of 202nd RAF sqn in Mediterranean Sea E off Cartagena. U75 was sunk 28.12.1941 by British destroyer Kipling in Mediterranean Sea N off Mersa Matruh. U76 was sunk 5.4.1941 by British destroyer Wolverine and sloop Scarborough in Northern Atlantic S off Iceland. U83 was sunk 4.3.1943 by Hudson of 500th RAF sqn in Mediterranean Sea SE off Cartagena. U84 after 7.8.1943 was lost in Northern Atlantic by unknown cause. U85 was sunk 14.4.1942 by American destroyer Roper at Cape Hatteras (US East Coast). U86 after 28.11.1943 was lost by unknown cause in Northern Atlantic. U87 was sunk 4.3.1943 by Canadian destroyer St. Croix and corvette Shediac in Northern Atlantic W off coast of Portugal. U99 was sunk 17.3.1941 by British destroyer Walker SE off Iceland. U100 was sunk 17.3.1941 by British destroyers Vanoc and Walker SE off Iceland.
U101 was sunk 3.5.1945 by Typhoons of 175th RAF sqn RAF at Neustadt. U102 was sunk 1.7.1940 by British destroyer Vansittart SW off Ireland.
Following submarines were scuttled by crews: U46 5.5.1945 in Flensburg Fjord; U48 3.5.1945 at Neustadt.
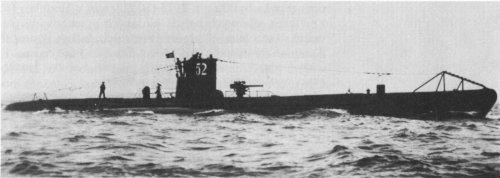
U52
© Ivan Gogin, 2008-14