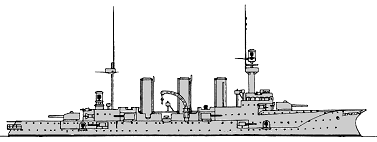

Victoria Louise 1898
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comp | Fate |
| Victoria Louise | 116 | Weser, Bremen | 1895 | 29.3.1897 | 20.2.1899 | TS 1908, minelayer / barrack ship 1915, discarded 10.1919 | |
| Hertha | 233 | Vulcan, Stettin | 1895 | 14.4.1897 | 23.7.1898 | TS 1908, barrack ship 1915 | |
| Freya | Danzig KW | 1895 | 27.4.1897 | 20.10.1898 | TS 1907, discarded 1.1920 | ||
| Vineta | Danzig KW | 1896 | 9.12.1897 | 13.9.1899 | test ship 1908, TS 1911, barrack ship 1915 | ||
| Hansa | 235 | Vulcan, Stettin | 1896 | 12.3.1898 | 20.4.1899 | TS 1909, barrack ship 1915 |
|
Displacement normal, t |
Victoria Louise, Hertha, Freya: 5660 Vineta, Hansa: 5885 |
|
Displacement full, t |
Victoria Louise, Hertha, Freya: 6491 Vineta, Hansa: 6705 |
|
Length, m |
Victoria Louise, Hertha, Freya: 110.6 oa 109.1 wl Vineta, Hansa: 110.5 oa 109.8 wl |
|
Breadth, m |
Victoria Louise, Hertha, Freya: 17.4 Vineta, Hansa: 17.6 |
|
Draught, m |
Victoria Louise: 6.58 mean 6.93 deep load Hertha: 6.58 mean 6.78 deep load Freya: 6.74 mean 6.77 deep load Vineta, Hansa: 7.08 mean 7.34 deep load |
|
No of shafts |
3 |
|
Machinery |
Victoria Louise, Vineta: 3 VTE, 12 Dürr boilers Hertha: 3 VTE, 12 Belleville boilers Freya: 3 VTE, 12 Niclausse boilers Hansa: 3 VTE, 18 Belleville boilers |
|
Power, h. p. |
10000 |
|
Max speed, kts |
Victoria Louise, Hertha, Freya: 19.5 Vineta, Hansa: 18.5 |
|
Fuel, t |
coal 950 |
|
Endurance, nm(kts) |
3412(12) |
| Armour, mm | deck: 40 with 100mm slopes, turrets: 100 - 30, casemates: 100, CT: 150 |
|
Armament |
2 x 1 - 209/37 SK L/40 C/97, 8 x 1 - 149/37 SK L/40 C/97, 10 x 1 - 88/27 SK L/30 C/89, 10 x 1 - 7.9/79, 3 - 450 TT (1 bow, 2 beam) |
|
Complement |
477 |
Project history: These protected cruisers show distinct affinities with contemporary German battleship designs, with fewer guns, more speed, and only a 100mm protective deck amidships, and die same protection for the turrets. They also introduced the rather massive appearance and the combined clipper and ram bow which were to mark the classes of German heavy cruiser up to the 1907 Scharnhorst. These ships, and their immediate successors, were rather top-heavy.
Ship protection: Protective deck was 40mm thick amidships and had 100mm slopes. CT had 150mm sides and 30mm roof. 21cm and 15cm turrets had 100m sides and 30mm crowns, casemates were protected by 100mm sides and 70mm bulkheads.
Modernizations: 1906, Victoria Louise; 1907, Freya; 1908, Hertha; 1909, Hansa; 1911, Vineta: boilers were replaced by 8 Marine, three funnels were replaced by two, the original tower foremast and fighting top were replaced by an ordinary pole mast; - 2 x 1 - 149/37, 10 x 1 - 7.9/79; + 1 x 1 - 88/27 SK L/30 C/89, 3 x 1 - 88/32 SK L/35 C/01
1916, Freya: was armed with 1 x 1 - 149/37 SK L/40 C/97, 4 x 1 - 105/42 SK L/45 C/11, 14 x 1 - 88/27 (SK L/30 C/89 and 88/32 SK L/35 C/01)
Naval service: In 1916 all the ships were disarmed and used for accommodation, except for Freya, employed as a schoolship, which retained armament. Victoria Louise underwent the unusual transformation in 1920 of conversion to the cargo ship Flora Sommerfeld for a Danzig Firm. She did not last long in her new guise, being broken up in 1923.
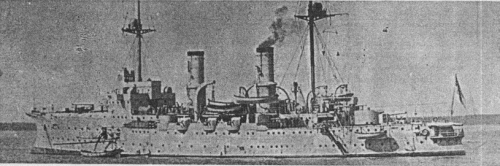
Hansa 1900s
© Ivan Gogin, 2014