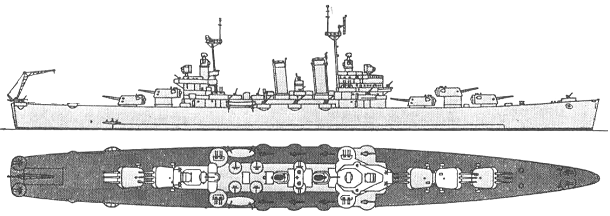

9 de Julio 1965
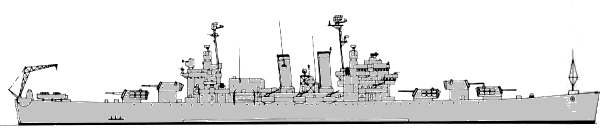
General Belgrano 1982
| Name | No | Yard No | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Comm | Fate |
| Diecisiete de Octubre (17 de Octubre) (ex-Phoenix), 9.1955- General Belgrano | C4 | 416 | New York SB, Camden, USA | 15.4.1935 | 12.3.1938 | 18.3.1939 // 5.12.1951 | sunk 2.5.1982 |
| Nueve de Julio (9 de Julio) (ex-Boise) | C5 | 361 | Newport News SB, USA | 1.4.1935 | 3.12.1936 | 1.2.1939 // 19.12.1951 | stricken 10.1977 |
|
Displacement standard, t |
C4: 10800 C5: 10500 |
|
Displacement full, t |
13645 |
|
Length, m |
182.9 wl 185.4 oa |
|
Breadth, m |
21.0 |
|
Draught, m |
7.30 max |
|
No of shafts |
4 |
|
Machinery |
4 sets Westinghouse geared steam turbines, 8 Babcock & Wilcox boilers |
|
Power, h. p. |
100000 |
|
Max speed, kts |
30 |
|
Fuel, t |
oil 2200 |
|
Endurance, nm (kts) |
7600(15) |
|
Armour, mm |
belt: 127 - 83, magazines belts: 51 (fore) - 120 (aft), bulkheads: 127 - 51, deck: 51, barbettes: 152, turrets: 165 - 32, CT: 127 sides, 57 roof |
|
Armament |
C4: 5 x 3 - 152/47 Mk 16, 8 x 1 - 127/25 Mk 27, 4 x 4 - 40/60 Mk 2, 6 x 2 - 40/60 Mk 1, 19 x 1 - 20/70 Mk 10, 2 helicopters C5: 5 x 3 - 152/47 Mk 16, 8 x 1 - 127/25 Mk 27, 4 x 4 - 40/60 Mk 2, 6 x 2 - 40/60 Mk 1, 2 helicopters |
|
Electronic equipment |
C4: SK, SG, Mk 3, 2x Mk 4 radars C5: SK, SG, Mk 13, 2x Mk 28 radars |
|
Complement |
868 |
Project history: General Belgrano was purchased by Argentina 12 April 1951, and refitted at the Philadelphia Navy Yard. The superstructure was reduced, bulges were added, the beam was increased and mainmast derricks and catapults were removed. The hangar in General Belgrano's hull could accommodate two helicopters with spare parts; the nearly flat counter and high freeboard aft provided an excellent helicopter platform.
iVitfiv de Juho was launched 3 December 1936, and was commissioned 19 December 1951. In the early 1960s, she, too, was fitted with a Dutch surface search radar. Decommissioned and stripped in 1978, she served as parts reservoir for her sister-ship and was scrapped in 1983.
Ship protection: Main belt abreast machinery was 4.2m high. It was 127mm thick (83mm at lower edge) on 16mm STS plating. There were narrow belts abreast magazines. Fore belt was 51mm thick but aft inner belt had 120mm thickness. Magazines were protected by 93mm bulkheads fore and aft, machinery and magazines were separated by 127-51mm bulkheads. Armoured deck over main belt was 51mm. Barbettes were 152mm thick. Turrets had 165-mm faces, 32-mm sides, 32-mm rears and 51-mm crowns.
Modernizations: early 1960s, both: new sensors consisted of LW-01, DA-01, Mk 33, Mk 34, 2x Mk 57, 2x Mk 63, NA9-D1 radars
1967, General Belgrano: + 2 x 4 Seacat GWS22 SAM (70? Seacat)
Naval service: During the Falklands conflict General Belgrano and two escorting destroyers were stationed to the southwest of the Falklands (Malvinas). She patrolled on a 200-mile line between Burwood Bank, S of the Falklands, and Isla de los Estados, E of Tierra del Fuego. On 2 May at 16.00 hrs local time she was torpedoed at a range of about 1.3km yards by British SSN Conqueror. At the time she was torpedoed, General Belgrano was approximately 220 miles from the Falklands sailing at 10kts toward the mainland. Two Mk8** torpedoes hit, the first under the aft 127mm gun director and the second just forward of A turret. The first hit tore the emergency generators from their foundations. The ship was without power. General Belgrano sank at 16.45 hrs; 321 lives were lost (95% killed by the torpedo hits) with the cruiser and 880 rescued after 24 hours in life rafts.

General Belgrano 1978
Many thanks to Wolfgang Stöhr for additional information on this page.
© Ivan Gogin, 2015